Reconstruction with DIEP and other free flaps
Free flaps involve microsurgery to transfer tissue from a part of the body to the chest to reconstruct the breast. There are 3 main free flaps: the DIEP, the gracilis flap and the PAP.
Book an appointment
The DIEP
The procedure for a DIEP reconstruction
The DIEP (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator) uses the excess skin and fat located on the abdomen, between the pubis and the navel. The vessels that irrigate this flap are the artery and the deep inferior epigastric vein. The rectus abdominis muscles (abdominal muscles) are left intact. The flap is transferred to the breast and the vessels reconnected near the breast. The abdomen is closed like a cosmetic tummy tuck, leaving a horizontal scar at the lower abdomen and a scar around the umbilicus.
This technique can be used for immediate or delayed breast reconstruction.
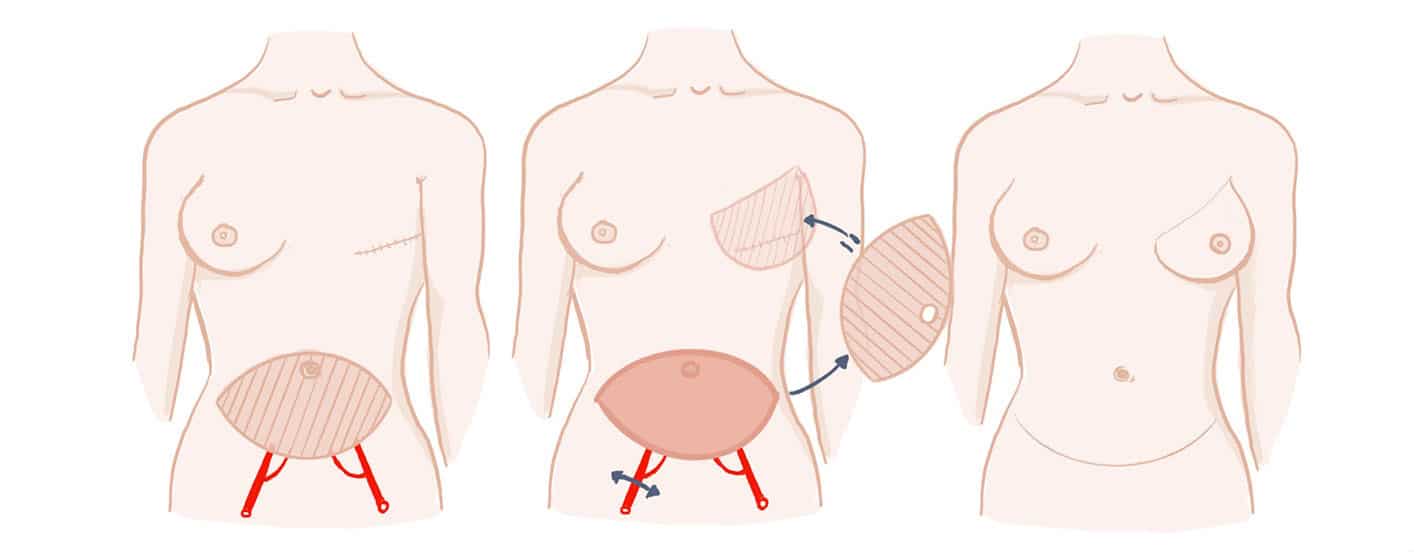
The benefits of DIEP
DIEP allows for the reconstruction of a very supple and natural breast.
In the case of excess skin and fat on the abdomen, it is sometimes possible to reconstruct a fairly large volume.
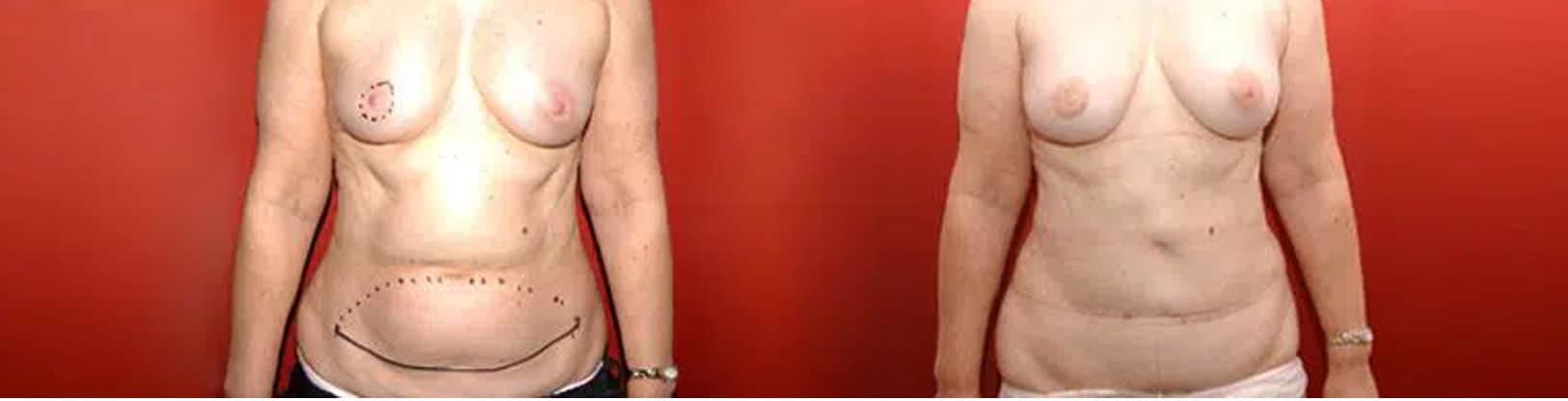
Right mastectomy and immediate reconstruction by DIEP
The disadvantages of DIEP
DIEP requires excess tissue on the belly and cannot be done in very thin women with “no belly”.
It is a long but minimally invasive surgery.
What is the aesthetic and functional result of a DIEP?
There are no functional or painful sequels on the abdomen. The skin of the abdomen has an appearance closer to that of the breast than that of the back. The visual and tactile aspect of the reconstructed breast is very natural, because it offers a non-fixed appearance, it is flexible and makes it possible to create a nice curve without the need for a prosthesis. The result follows you over time, because the reconstruction is permanent, there are no implants to change. Similarly, the DIEP will follow your weight variations, if you lose weight, it will lose weight, if you gain weight, it will gain weight. Pregnancy is possible after a DIEP. Finally, the silhouette is improved by the removal of the flap as a cosmetic tummy tuck.
Before / After DIEP reconstruction
Below are photos illustrating the results of several immediate and delayed DIEP breast reconstructions.
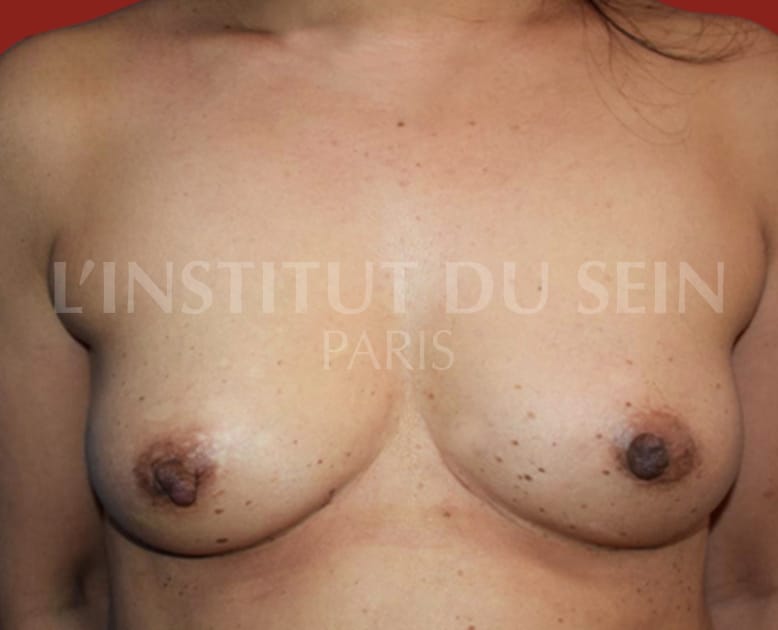
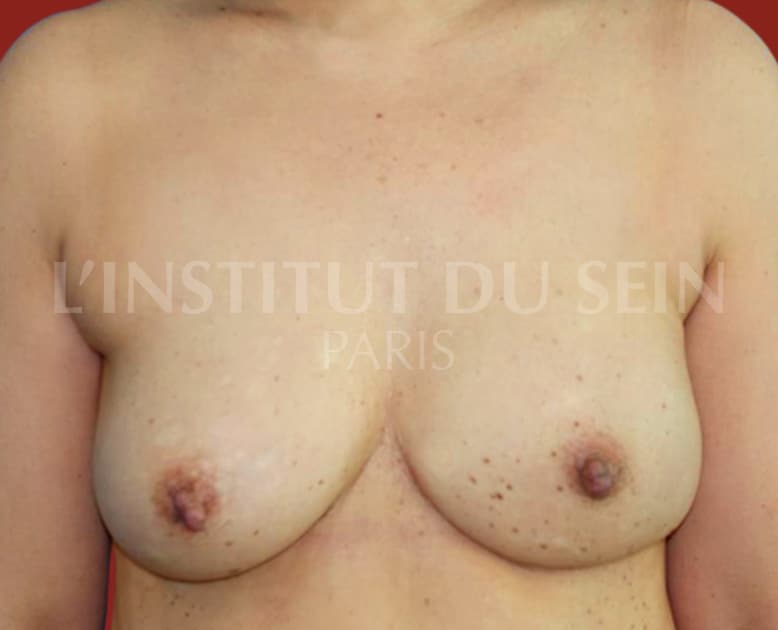
1.1. Immediate reconstruction of the left breast by DIEP.
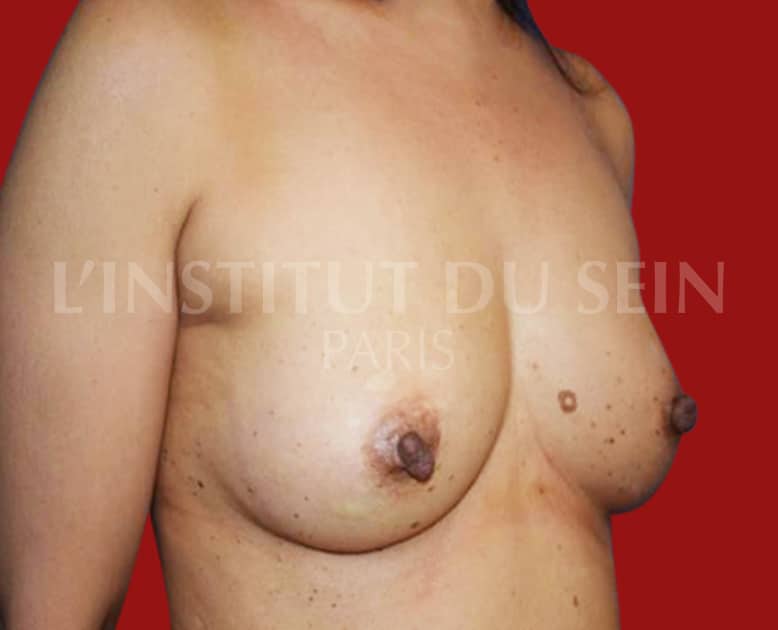
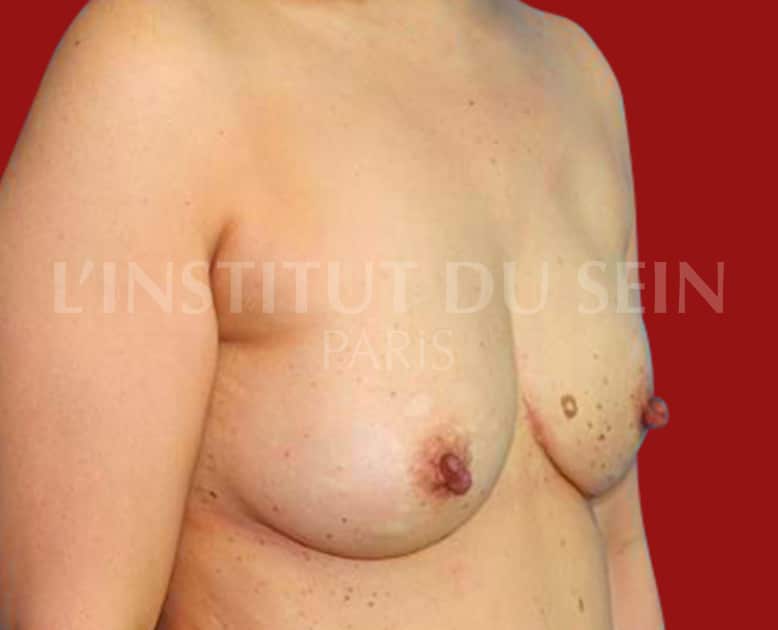
1.2. Immediate reconstruction of the left breast by DIEP.
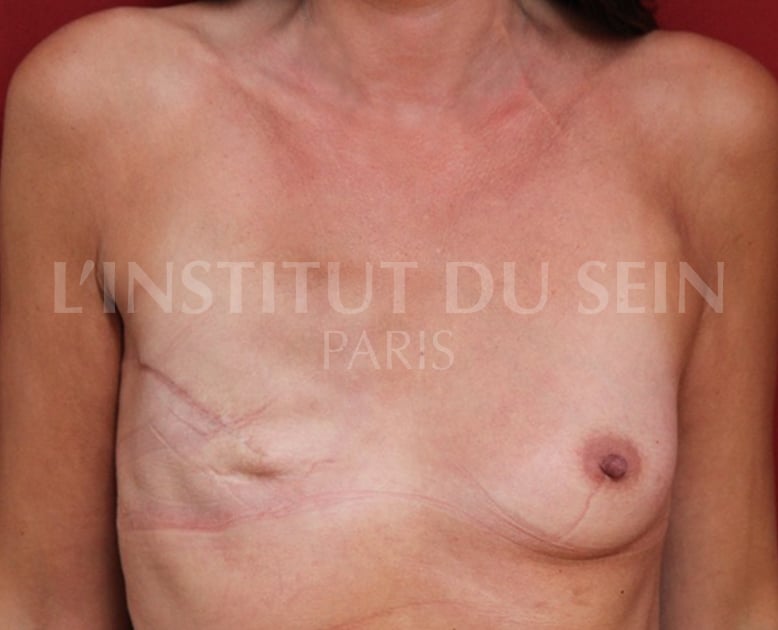
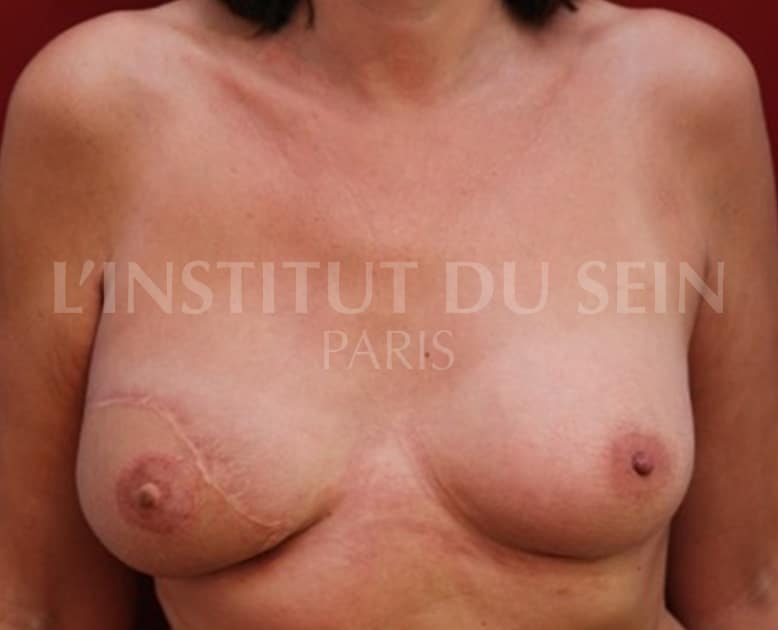
2. Reconstruction of the right breast by DIEP. Augmentation of the left breast.
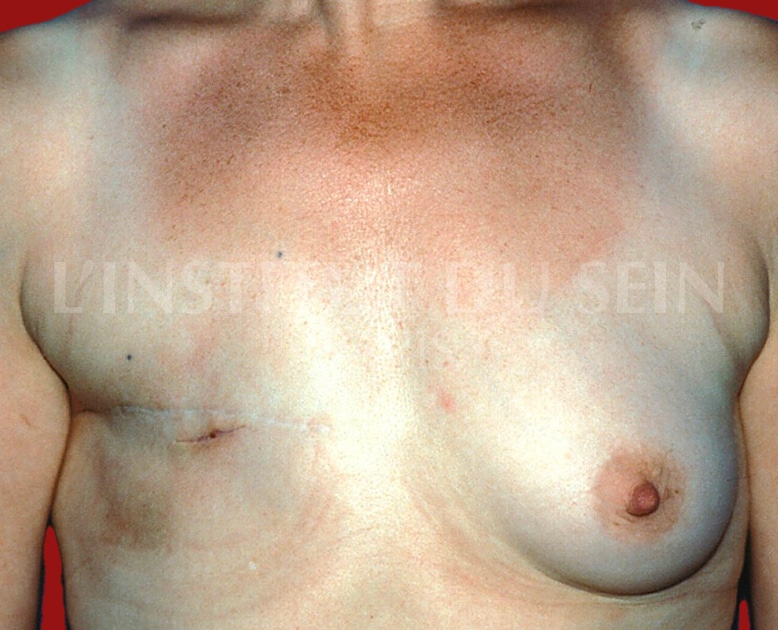
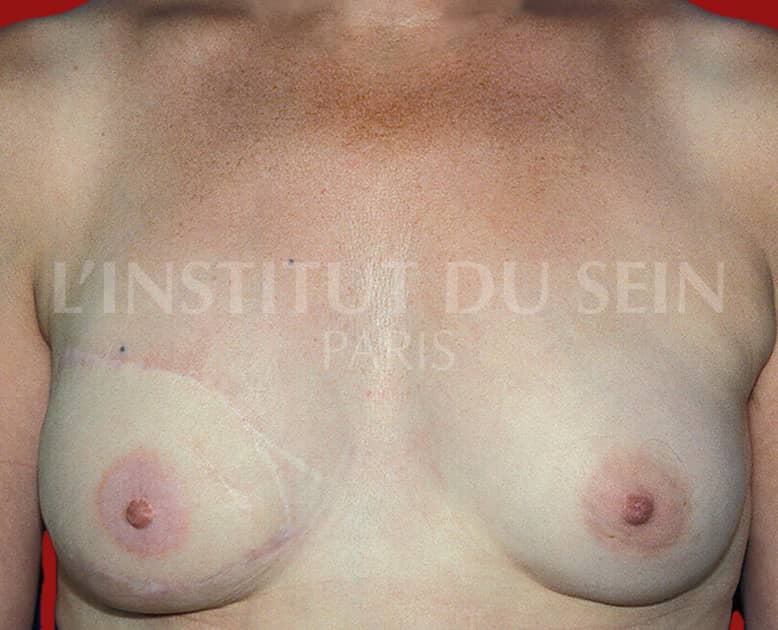
3. Straight reconstruction by DIEP.
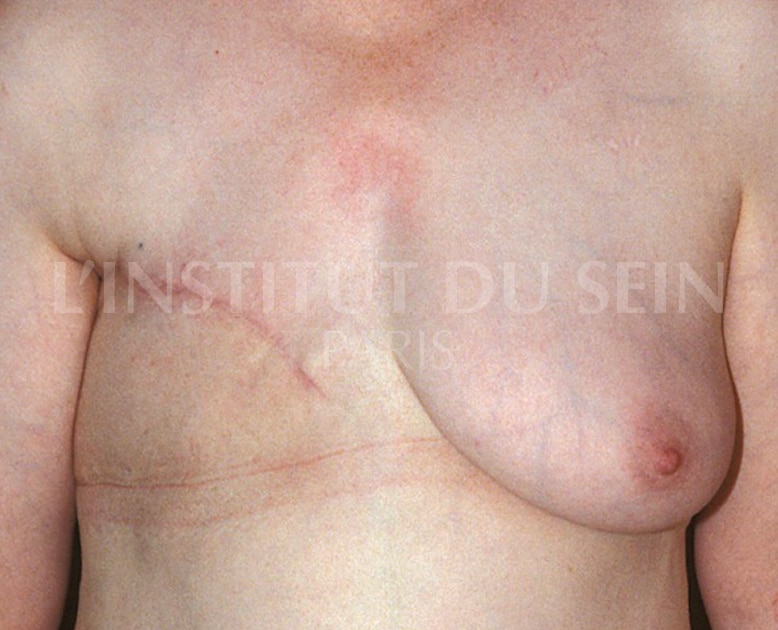
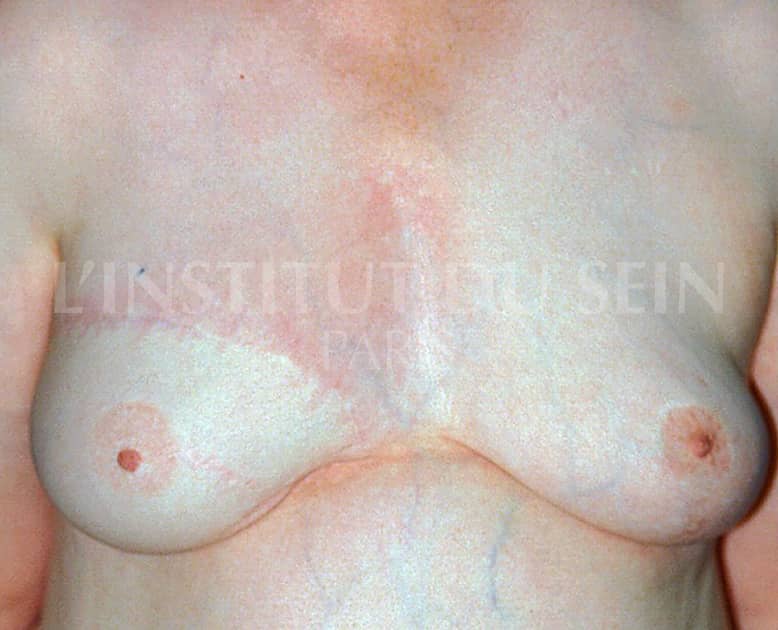
4. Right reconstruction by DIEP and reduction mammoplasty on the left.
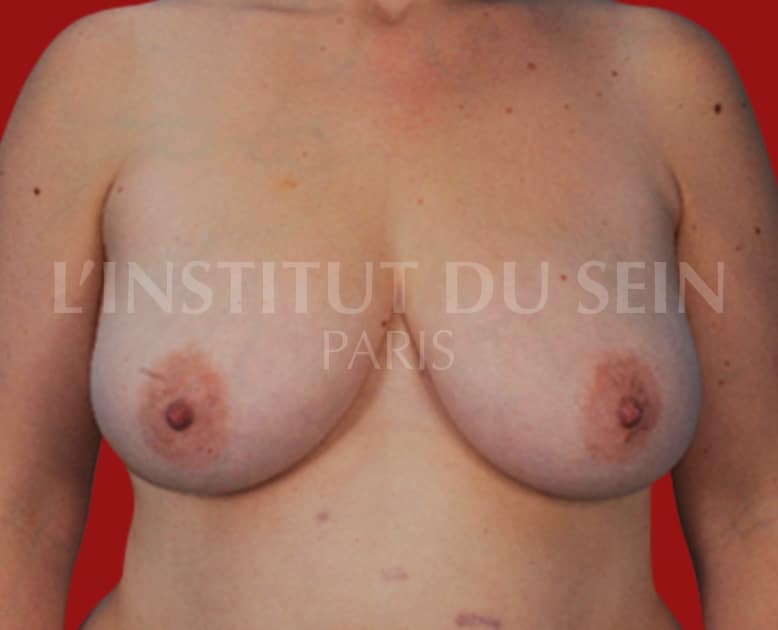
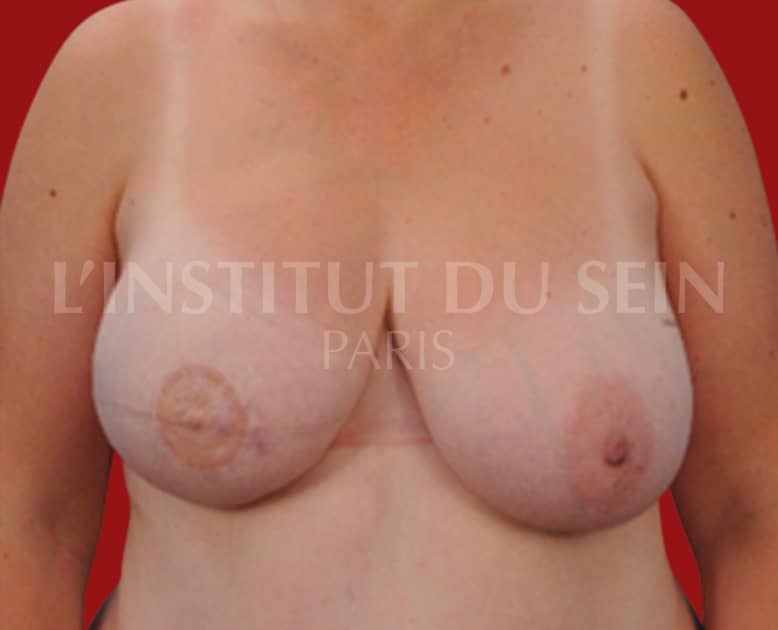
5.1. Immediate right reconstruction by DIEP.
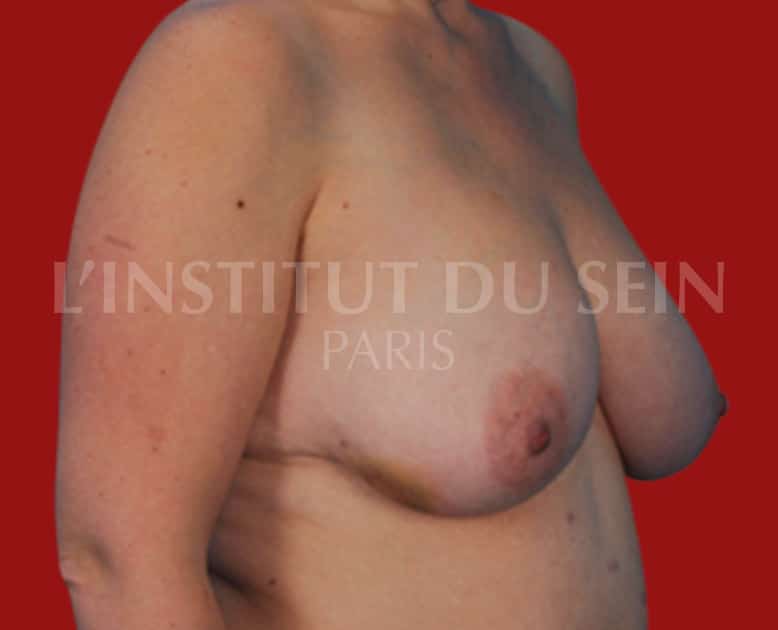
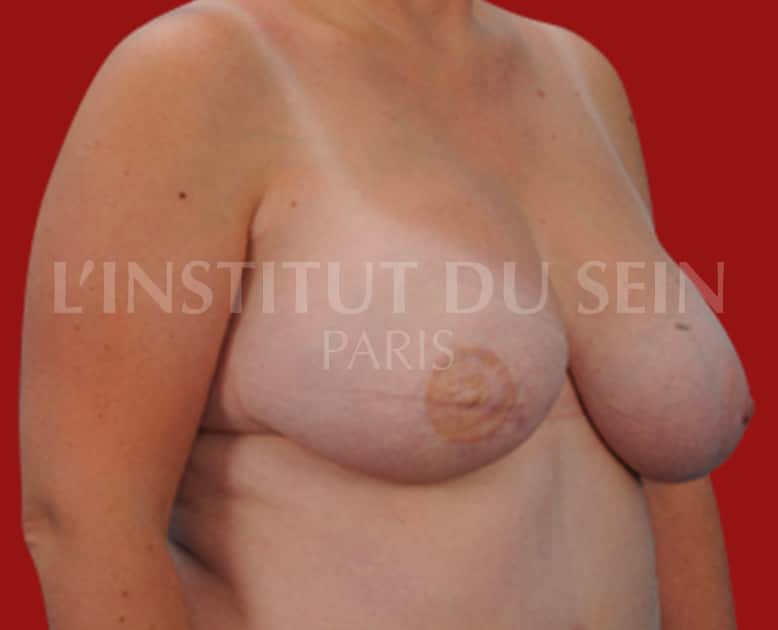
5.2. Immediate straight reconstruction by DIEP.
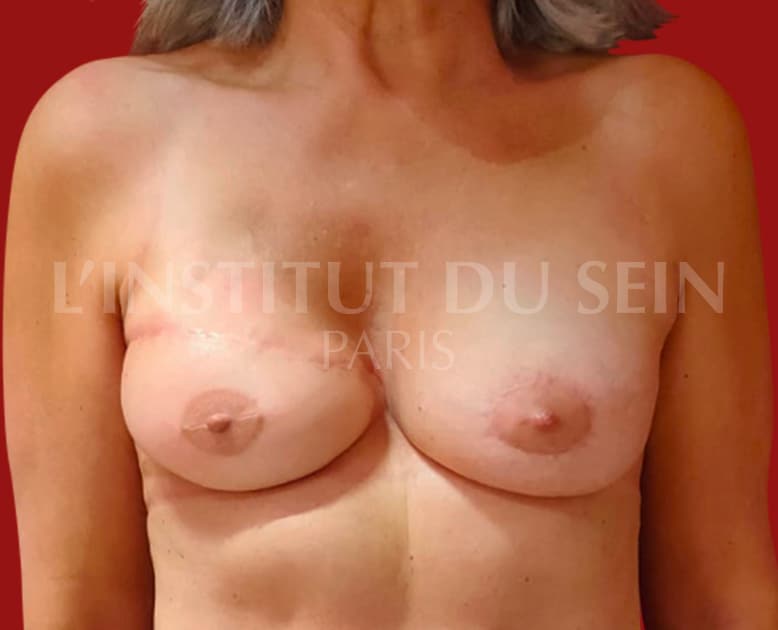
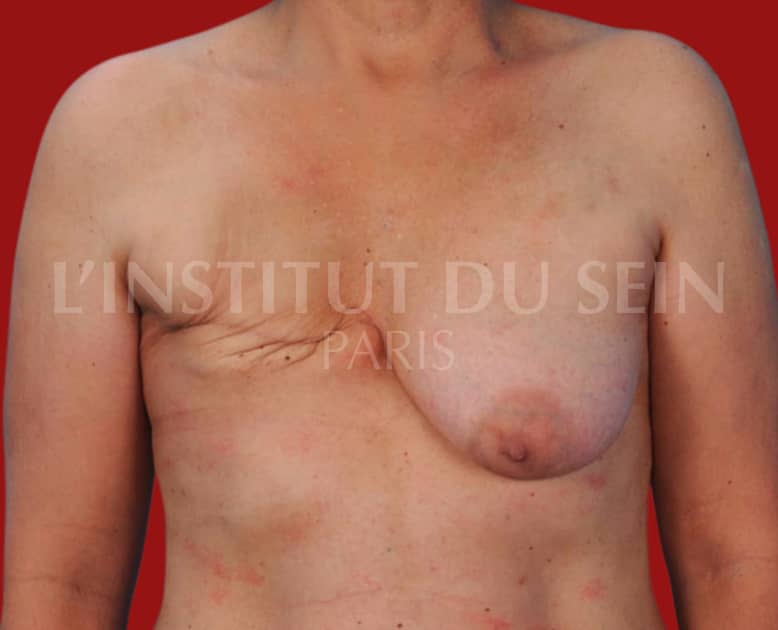

6.1. Right reconstruction by DIEP and augmentation of the left breast by prosthesis with treatment of the ptosis.
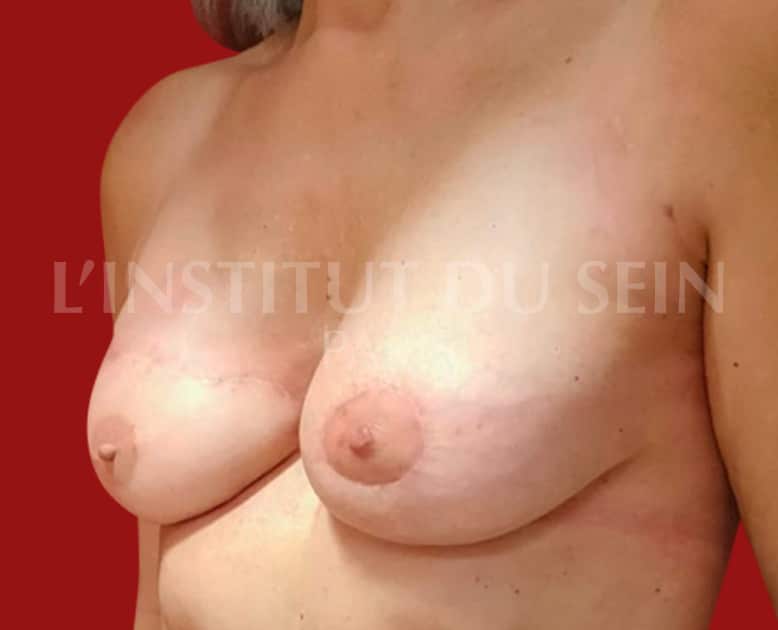
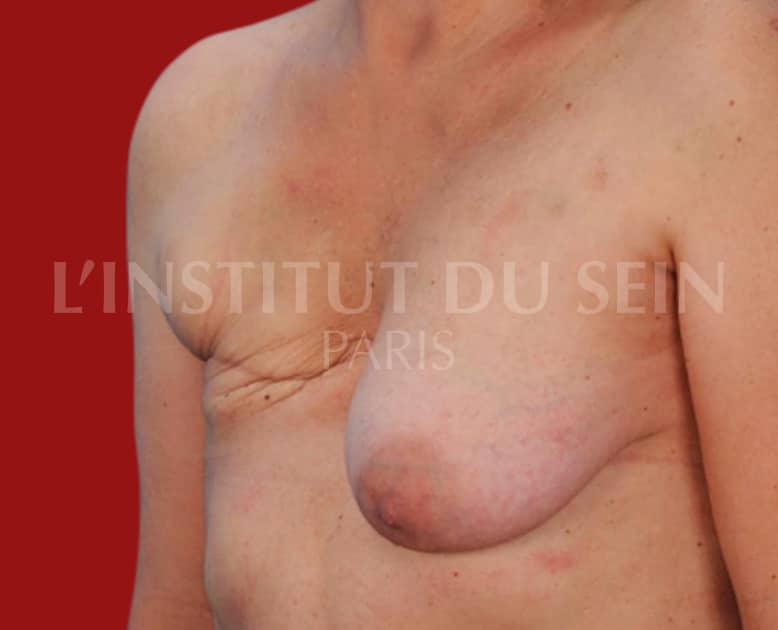

6.2. Right reconstruction by DIEP and augmentation of the left breast by prosthesis with treatment of the ptosis.
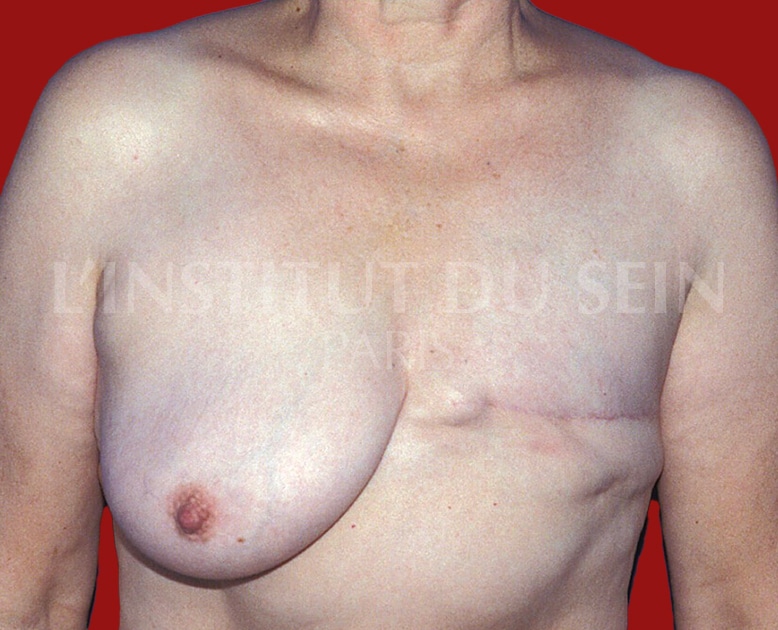
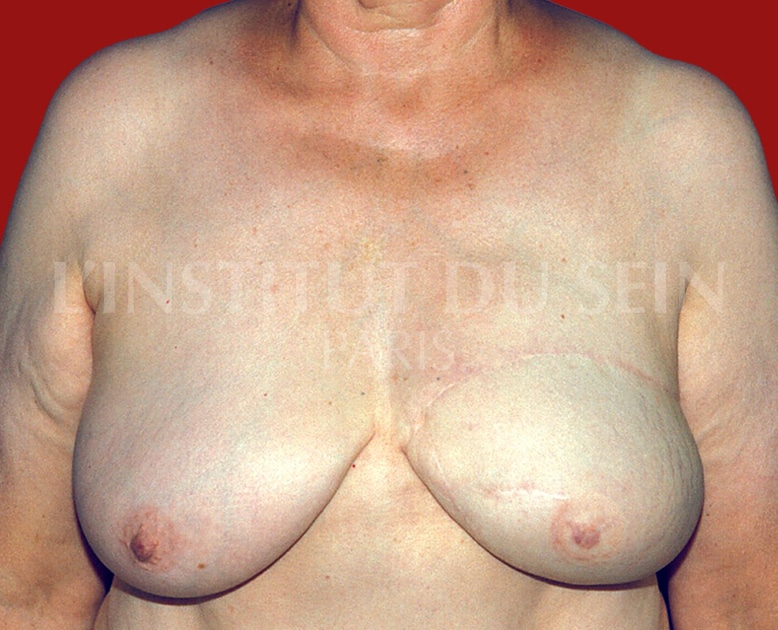
7. Left reconstruction by DIEP.
The PAP
The procedure for a PAP reconstruction
The PAP flap is a removal of the excess skin and fat from the top of the inner and posterior surface of the thigh. The skin and fat are harvested from the top of the posteromedial aspect of the thigh with its vessels (artery and vein). The flap is then reconnected to the thorax by microsurgery.
Benefits of the PAP
It does not require muscle harvesting as for the Gracilis thigh flap. It can be performed on women with slender morphologies who are not candidates for DIEP. Reconstruction is natural, as there is no implant.
The disadvantages of the PAP
The scar is located at the root of the thigh and can be painful and unsightly. The amount of skin and volume is limited and is mainly intended for small breast volumes. The color of the skin of the thigh being darker than that of the breast, the PAP is mainly used when it can be buried under the skin of the breast (during an immediate breast reconstruction or after changing an expander or prosthesis).
The GRACILIS or TUG
The free gracilis flap is a removal of skin, fat and a small accessory muscle (the gracilis) on the inner side of the thigh root. The Gracilis muscle is a long and thin muscle running from the pubis to the inner side of the knee. Its removal allows the volume of the reconstruction to be increased. As with the other free flaps, the TUG is reattached to the thorax by microsurgery.
The advantages of GRACILIS
The procedure is feasible for most women, even if the excess of the inner thigh appears moderate. The reconstructed breast will be of medium volume (most often B cup). The scars are placed at the root of the thigh, in the genitocrural fold and in the gluteal fold. Like the PAP, the gracilis can be performed on women with thin morphologies who are not candidates for the DIEP and will be used buried under the skin of the breast.
The disadvantages of GRACILIS
The removal of the muscle does not result in functional sequelae, but the scar may be painful and unsightly.
Modalities of the GRACILIS intervention
- The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
- The procedure takes about 4 to 7 hours for the reconstruction of a breast. The time is increased in case of bilateral reconstruction (8 to 10 hours).
- The hospitalization lasts from 5 to 8 days.
- Close monitoring is essential during the first 24 hours following the operation. The flap must be monitored to verify that it is well vascularized, this is verified by skin recoloration and heat and a Doppler signal. After one week, complications are extremely rare.
- The dressings, renewed daily, are kept for at least 15 days.
- The recovery lasts about 1 to 2 months.
- It is necessary to wear an abdominal girdle for 6 weeks for the DIEP.
- Antithrombotic stockings will have to be worn for 15 days and anticoagulant injections (Lovenox®) will have to be given for 15 days to prevent the risk of phlebitis.
- Resumption of sports is possible approximately 3 months after surgery.
Possible complications after a GRACILIS
- The reconnected vessels may become blocked and thrombosed, and blood no longer flows. This implies an emergency surgery to try to save the reconstruction. If revascularization of the flap is impossible, the flap will necrose, which will lead to its total loss. The risk of total failure is about 5%.
- In some cases, there is partial necrosis of the flap which may cause a loss of volume in certain areas of the reconstructed breast.
- Healing can be long in some cases.
Contraindications to free flaps
- Smoking because of the risk of vascular complications of the flap and delayed healing.
- Obesity because of the increased risk of thromboembolism and delayed wound healing.
- Surgical procedures at the donor site (abdomen for DIEP, thigh for gracilis and PAP).
- Contraindications related to the general state of health.





Leave your comment