Breast augmentation with prostheses
Breast augmentation with prostheses is one of the most widely practiced cosmetic procedures in the world. At the Paris Breast Center, our goal is to provide you with breasts that stay natural.
Book an appointment
General
More than 500,000 French women have breast implants. Doctors have more than 60 years of experience with silicone implants (even though this material has evolved a lot since the first model in the 1960s) and a great knowledge of their long-term effects.
Breast prostheses :
- Do not cause breast cancer
- Do not interfere with cancer screening
- Do not affect pregnancies
- Do not interfere with breastfeeding
- It is sometimes useful to conceal the outline of the prosthesis with lipofilling
Characteristics of a breast augmentation with implants procedure
- The intervention takes from 1 hour to 1 hour 30 minutes.
- A general anesthesia is performed.
- The procedure is done on an outpatient basis (the patient is discharged the same day) or with an overnight hospital stay.
- Dressings are required for about 8 days.
- Wearing a sports bra is recommended for 3 weeks.
- Sports are contraindicated for about 3 weeks.
This operation can be covered by the Social Security in case of agenesis (total absence of breasts), asymmetry or breast deformities. A request for prior agreement is sent to your health insurance fund.
The scars of the implant placement of a breast augmentation
According to your morphology and your desire, 3 incisions are possible:
- Under the areola. The scar is at the junction of the areola and the skin of the breast: it is barely visible.
- Under the breast. This is the most suitable method if the areolas are very small or if the breasts fall slightly on the submammary fold.
- Under the arm. Very rarely used, because perfect positioning of the prosthesis is difficult with this route and replacing prosthesis is more complicated.
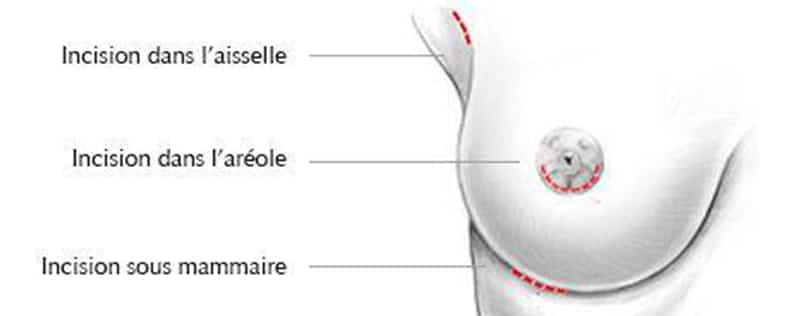
The location of the breast prostheses
- In front of the pectoral muscle (left drawing) ; In order for the prosthesis to not be visible it is necessary for the mammary gland to be sufficiently developed or that enough fat is present in the cleavage area. It is possible to combine a filling (autograft of fat) to conceal the outlines of the prosthesis.
- Behind the pectoral muscle (right drawing) ; the prosthesis is placed in what surgeons call a “dual plane”: the upper part of the prosthesis is behind the pectoral muscle, and the lower part is behind the gland. The pectoral allows the prosthesis to be concealed in the cleavage area.
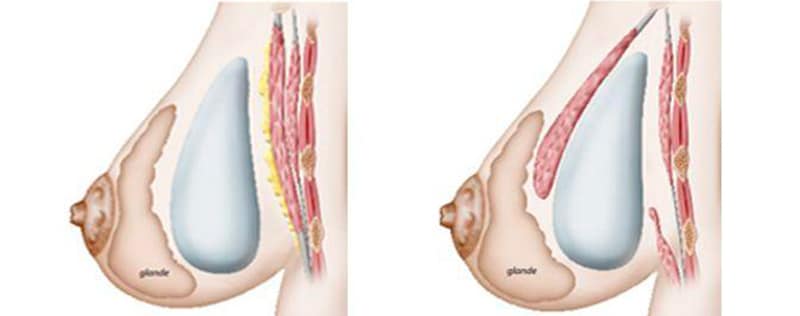
On the left : Pre-pectoral prosthesis. On the right : retro-pectoral prosthesis (dual plane)
The different types of prostheses
There are two filling materials: silicone gel and physiological serum. Silicone gel-filled prostheses are the most commonly used.
The envelope of the prostheses is always made of silicone. A distinction is made between smooth and microtextured prostheses.
The shape of the prosthesis can be round or anatomical
The choice is made according to the anatomy of the chest (its width, its height, the flexibility of the skin, the volume of the breasts before the operation) and the desired results of the patient.

Round prostheses

Anatomical prostheses
As with any surgical procedure, the insertion of prostheses can create side effects.
Postoperative complications are very rare
- Hematoma : usually occurs within the first 24 hours.
- Infection : this is treated with antibiotics, but may require the removal of the prosthesis in very rare cases, which can then be replaced a few months later.
- Decrease or loss of nipple sensitivity.
- The asymmetry in implant positioning, which is rare, may require some revision surgery.
Late complications
- The rupture of the prosthesis : breast implants have a limited lifespan, which varies according to the prosthesis and the person. Rupture is very rare before 10 years, and most often occurs between 10 and 20 years after insertion, but some implants are still intact after 25 years: there is therefore no requirement to change implants “preventively”. The wearing of breast implants requires an annual ultrasound follow-up. As rupture of the prosthesis usually does not show any sign, the prosthesis should be changed when the radiologist indicates that the prosthesis has ruptured. A ruptured prosthesis should be changed without urgency. Do not hesitate to get two opinions, as the diagnosis of a rupture is sometimes incorrect.
- The shells : a scar always forms around the implant (capsule). Sometimes this capsule becomes rigid. It then forms a shell that squeezes the prosthesis and can modify the appearance of the breast, which appears deformed. This occurs in about 5% of cases. The shell is not dangerous, but it can be aesthetically embarrassing, particularly because of the asymmetry. A reoperation can often improve the result.
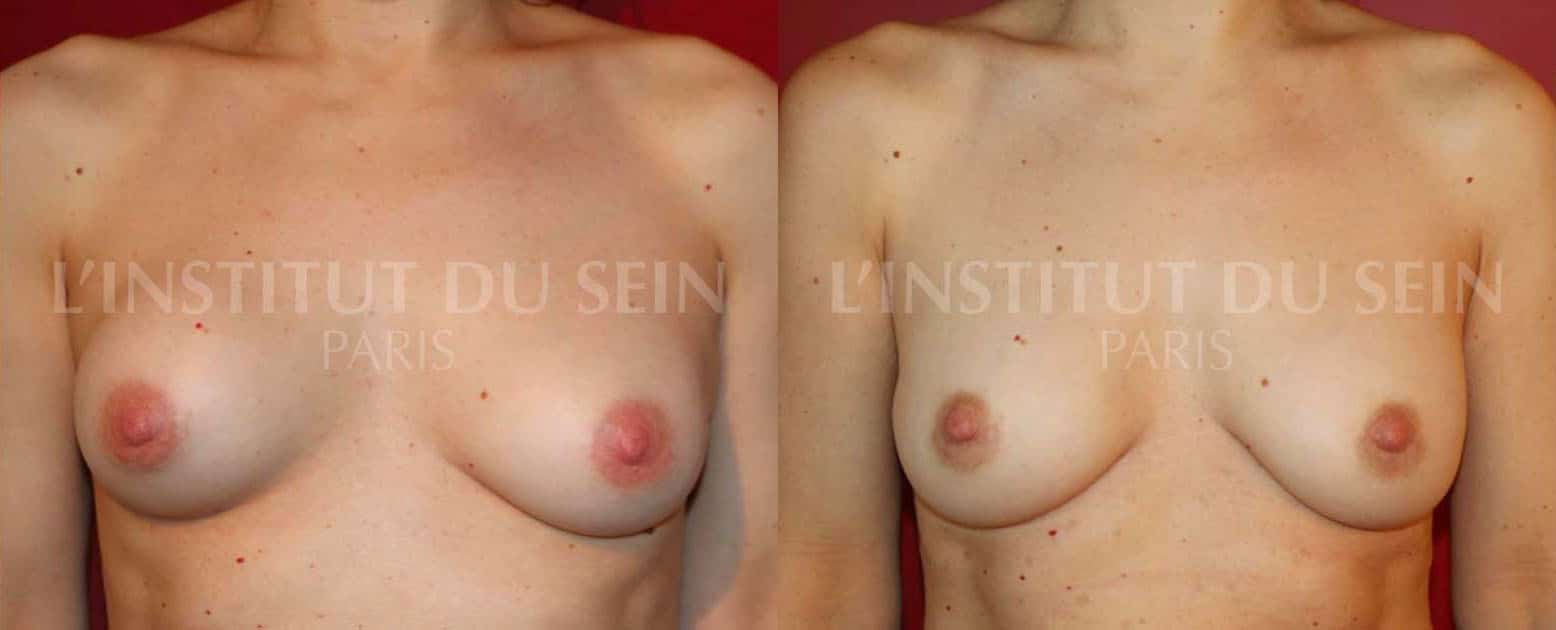
Before/After: Shell of the right breast. Correction by change of prosthesis
- Changes of the breast over time : breasts change during your life: they increase at puberty, then vary with your weight, pregnancies, breastfeeding, and at menopause. The results of cosmetic surgery will be modified by these events, which may require a reoperation. We help a lot of patients for aesthetic improvement, sometimes 10 or 20 years after their prosthesis was placed.
- Complications related to the prosthesis itself
Current situation of the March 2019 ANSM ban regarding all macro-textured prostheses.


Leave your comment