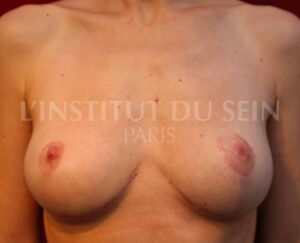
Breast ptosis
Breast ptosis is when the breast is sagging and is empty in its upper part.
Book an appointment
What is breast ptosis?
Breasts are said to be affected by “ptosis” when they are sagging.
This aesthetic problem covers different situations depending on two variables: the amount of skin and the volume of the breasts. The surgical technique is adapted on a case-by-case basis, depending on the morphology of the breasts.
There are several types of ptosis:
1. Empty breasts
This is common following a pregnancy or weight loss. It is possible to increase the volume of the breasts (with a filling or with prostheses) without reducing the amount of skin by limiting the scars.


Augmentation by prosthesis
2. The amount of skin is excessive, with a lack of volume.
The volume of the breast must be increased and the skin must be lifted during the same operation.

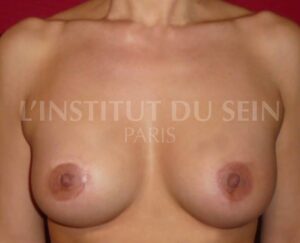
Augmentation by prosthesis + eriareolar lift
3. The amount of skin is excessive but the breast volume is satisfactory.
In this case, the surgeon can lift the skin, without changing the volume.
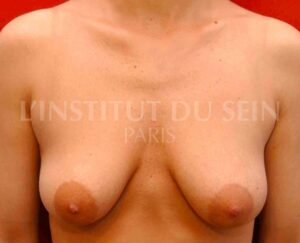
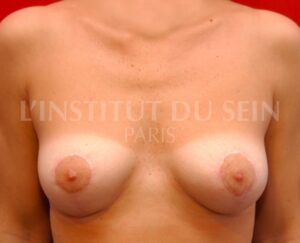
Lifting by inverted “T” mastopexy
4. The amount of skin is excessive and the volume is too large.
The surgeon reduces the volume and lift the skin as in a breast reduction surgery.
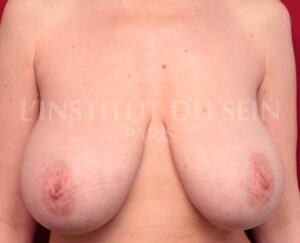
Breast lift and reduction
Scars after a breast ptosis treatment
The length of the scars depends on the amount of excess skin.
The goal is always to limit the length of the scars. This should not be done at the expense of the quality of the result, in particular the shape of the breast. It is better to have scars that are a little longer but less visible than wide scars with a poor shape correction.
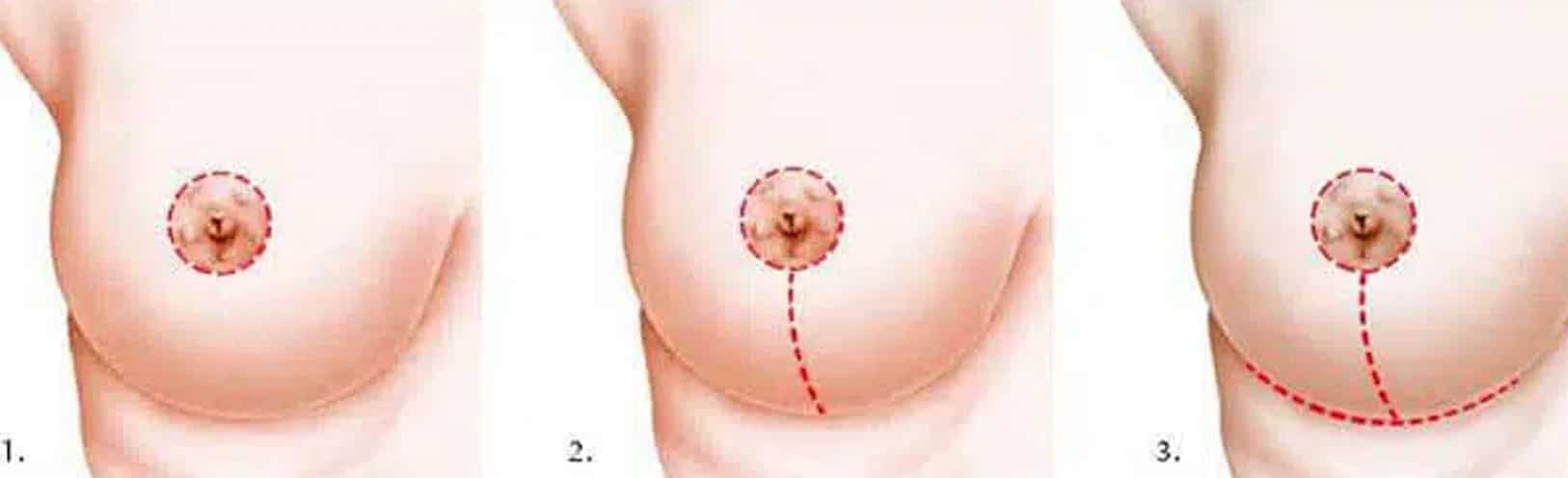
1. Periareolar scar
2. Periareolar and vertical scar
3. Periareolar scar, vertical and a scar in the sub mammary fold called inverted-T scar

The quality of the scars depends on the way each patient heals. All of the patients above have T-shaped scars (figure 2) and one year of healing: as you can see the healing is different for each one.
Characteristics of the breast ptosis surgery
- The procedure takes 1h30 under general anesthesia, or exceptionally under local anesthesia.
- Hospitalization is most often done on an outpatient basis (same day discharge).
- The surgical outcome is not painful.
- The dressings are kept for 8 days.
- Few days off work (not covered by social security).
- No exercise for 2 to 4 weeks.
Possible complications after breast ptosis surgery
They are related to the healing process.
Post-operative complications
Favored by smoking. It is advisable to stop smoking 1 month before and after the operation.
- Necrosis of a part of the areola or gland.
- Disruption of a scar or infection.
- Decrease or loss of sensitivity of the areolas and nipples.
Late complications
- Unsightly scars: hypertrophic, keloids or misplaced.
- Recurrence of ptosis on very thin skin or when there are weight changes.
- Residual asymmetry.
Before / After breast ptosis surgery
Below are a few photos illustrating the results of several ptosis correction procedures.


1. Treatment of ptosis by inverted T-scar.
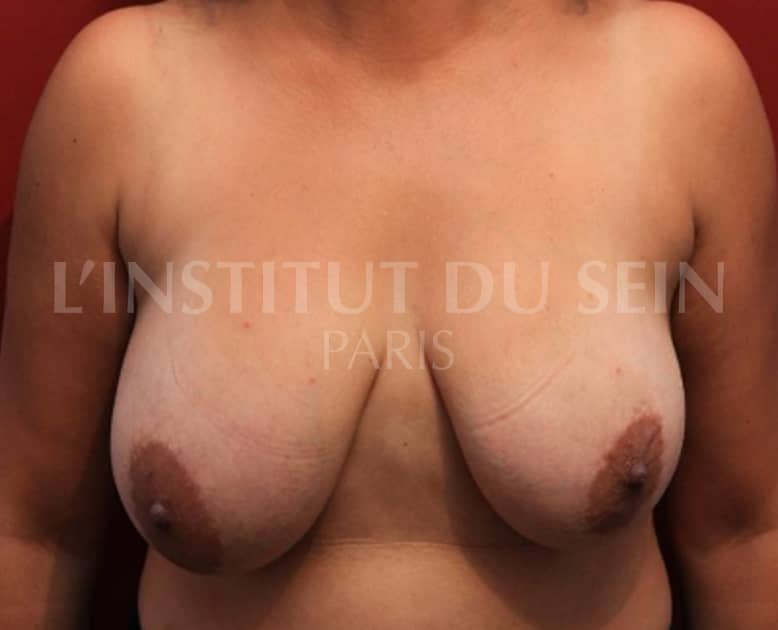
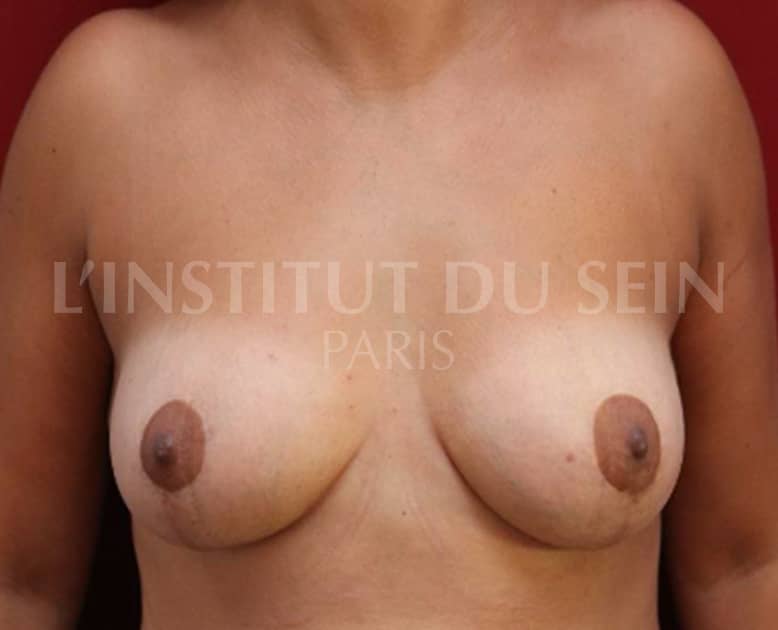
2. Treatment of ptosis, correction of hypertrophy and asymmetry by inverted T-scar
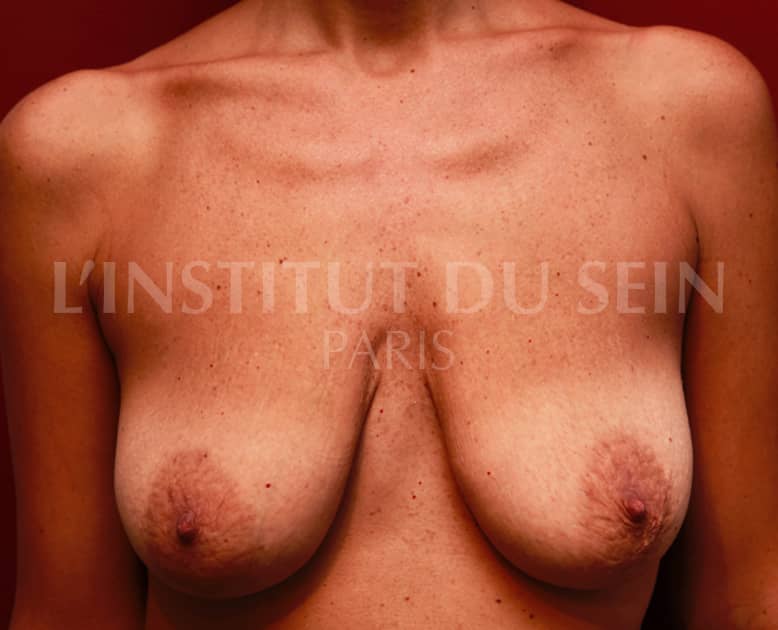
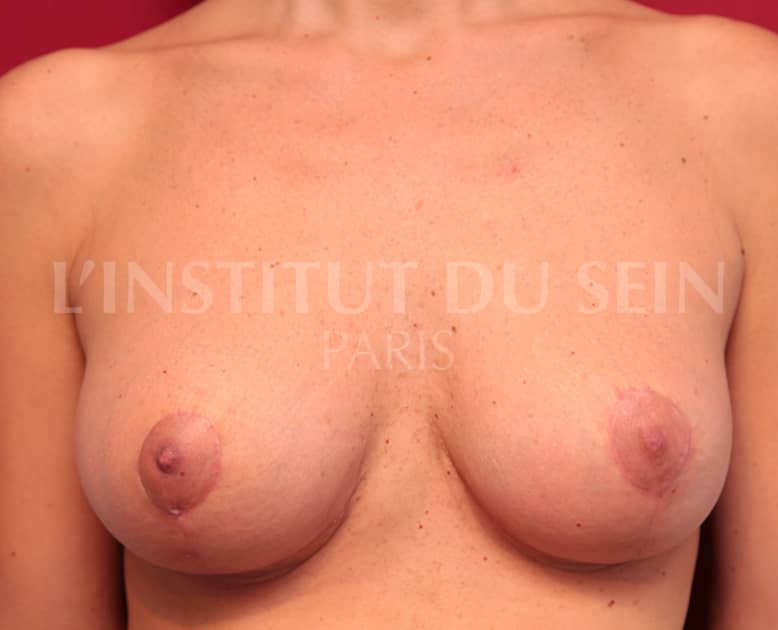
3. Treatment of ptosis. Increase by lipofilling. Inverted T-scar.
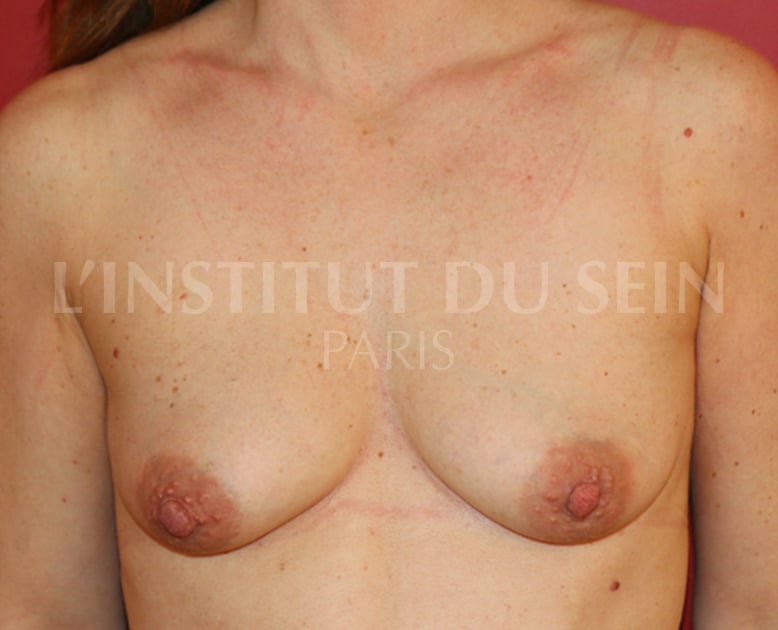
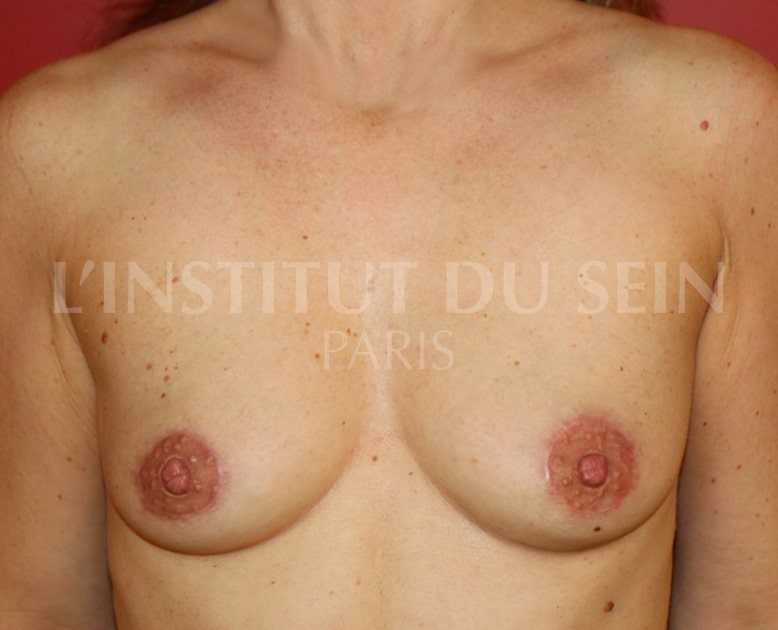
4. Treatment of ptosis. Scar around the areolas only (Round Block).
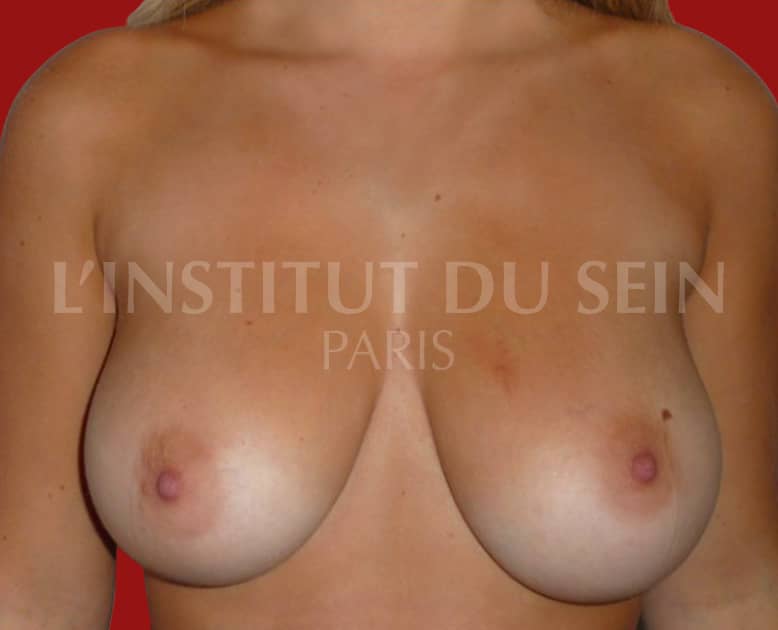

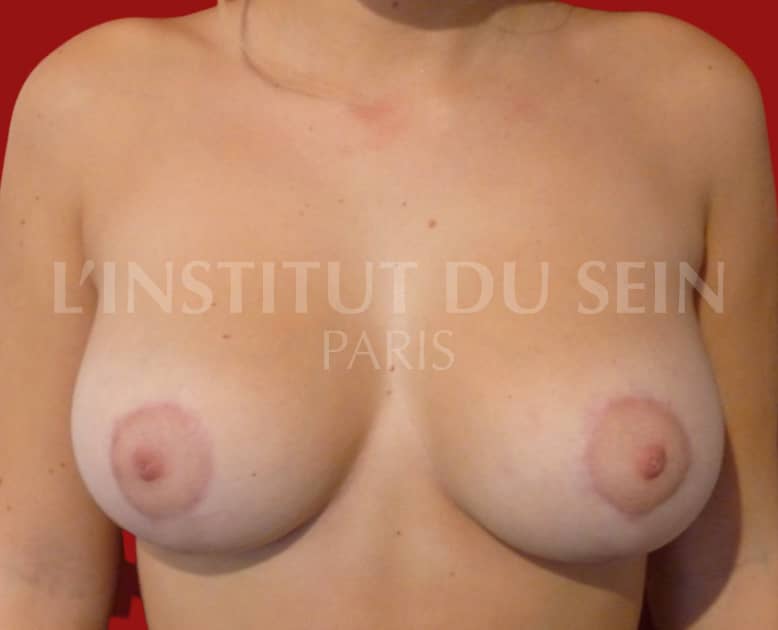
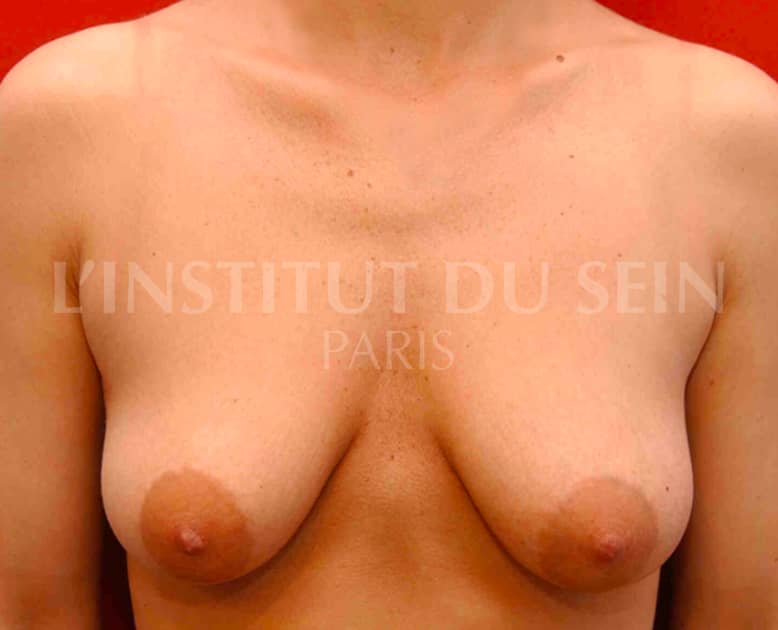
5. Treatment of ptosis and correction of hypertrophy and asymmetry. Inverted T-scar.
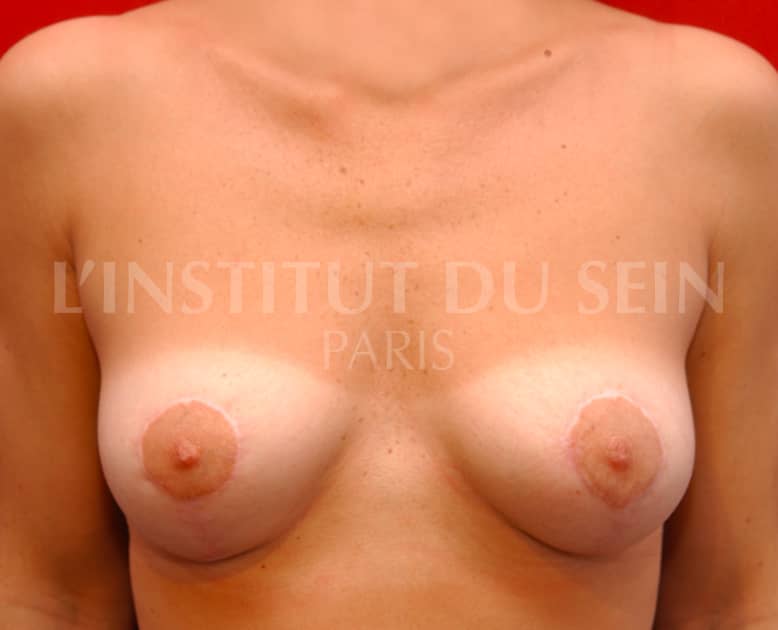
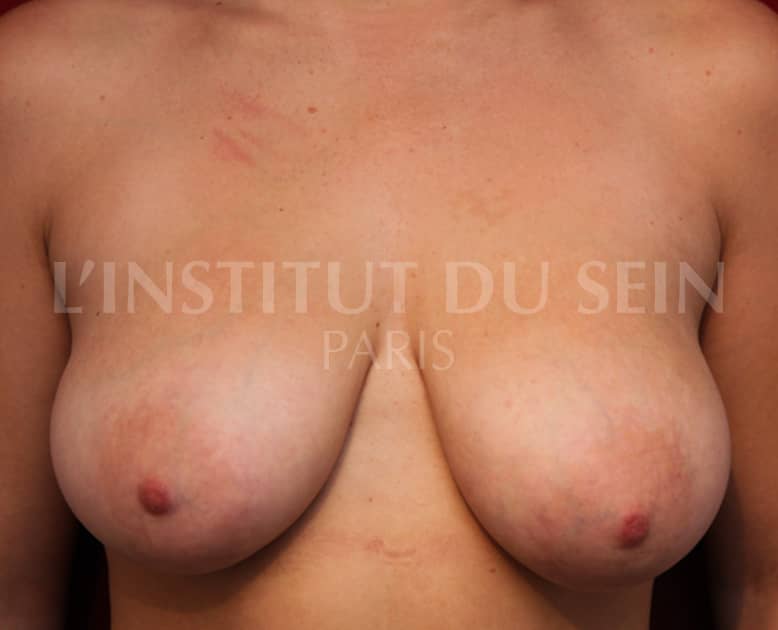
6. Treatment of ptosis. Inverted T-scar.
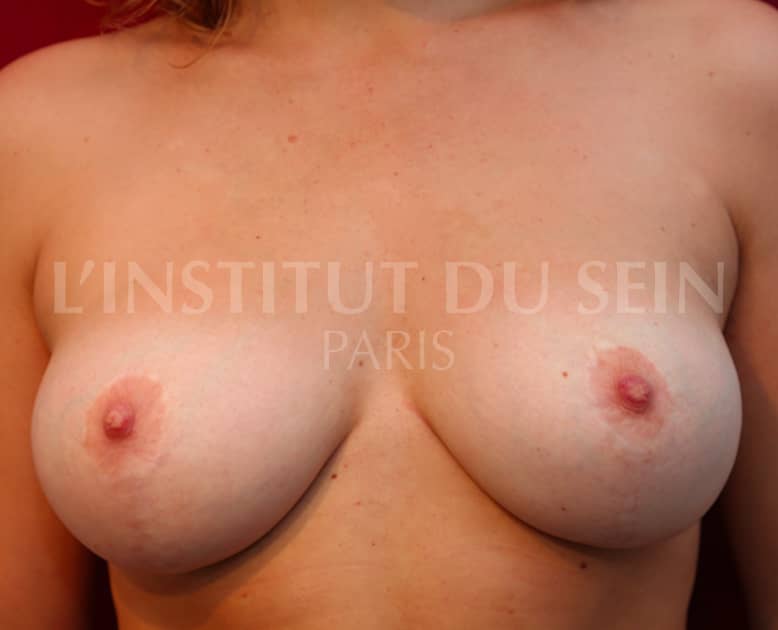

7. Treatment of ptosis. Inverted T-scar.
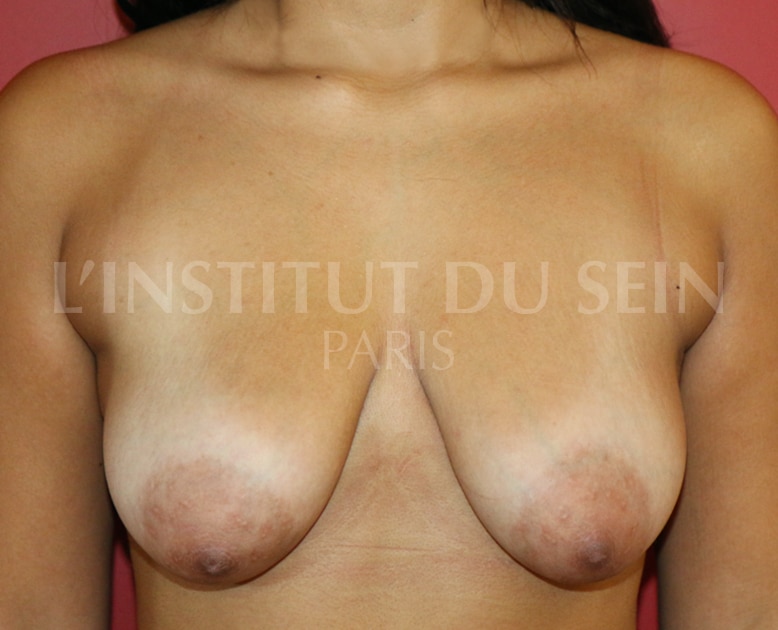
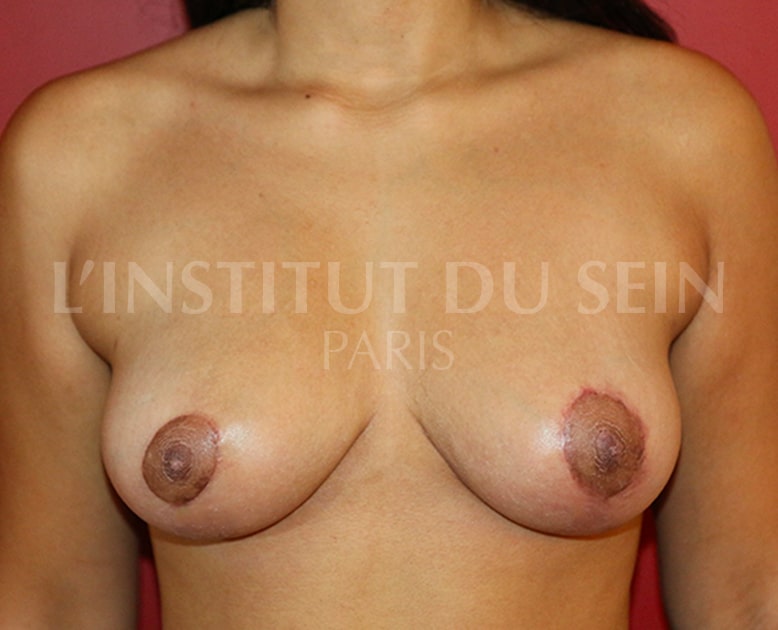
8. Treatment of ptosis. Inverted T-scar.
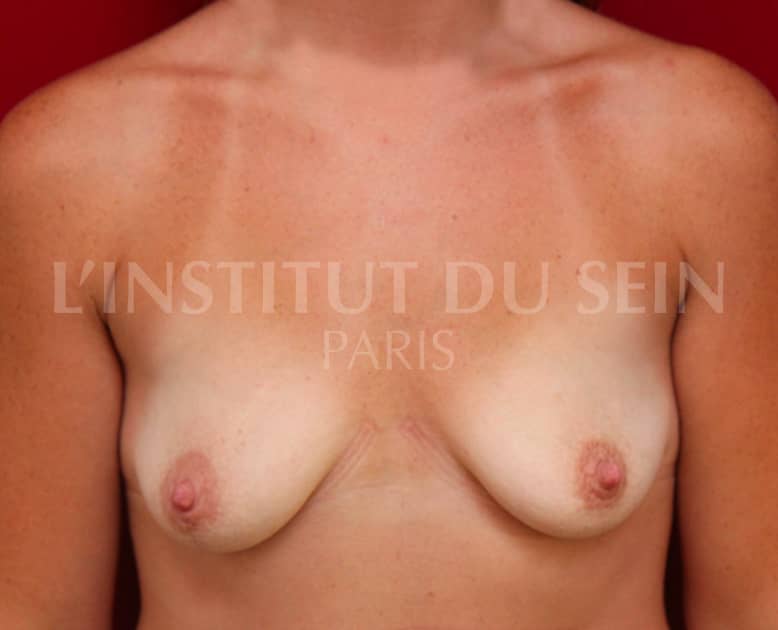
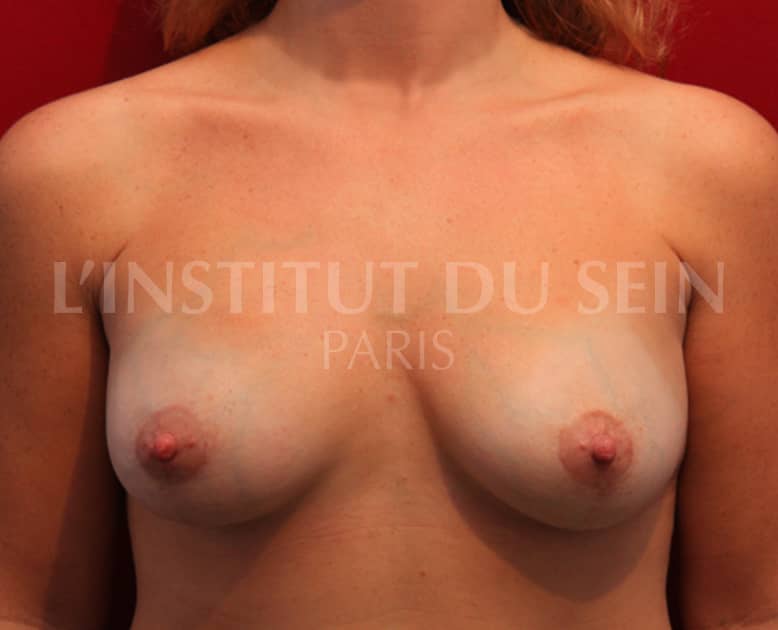


9.1 Treatment of ptosis by inverted T-scar. Augmentation by prostheses. Lipofilling.
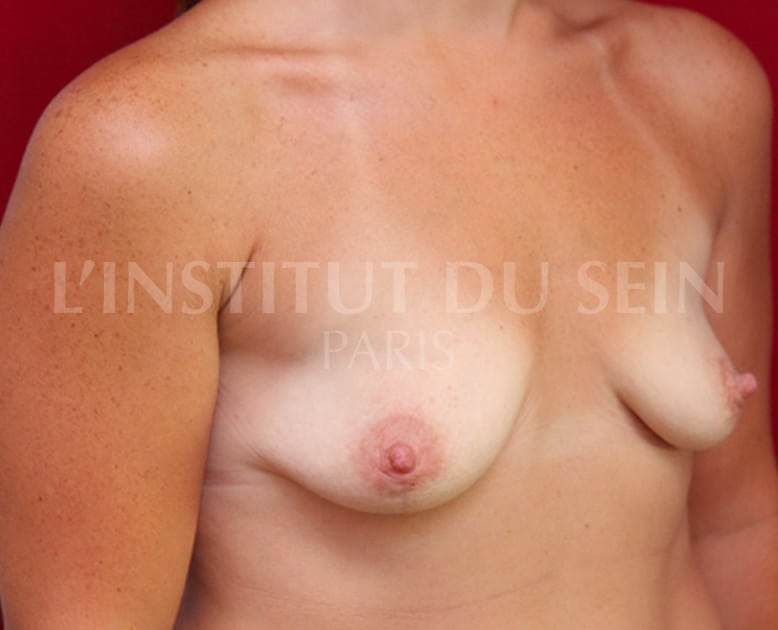

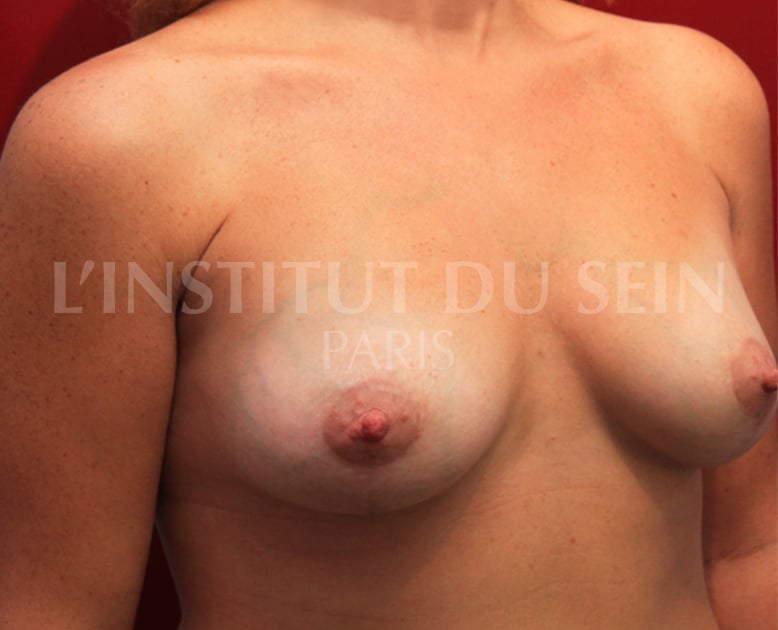
9.2 Treatment of ptosis by inverted T-scar. Augmentation by prostheses. Lipofilling.
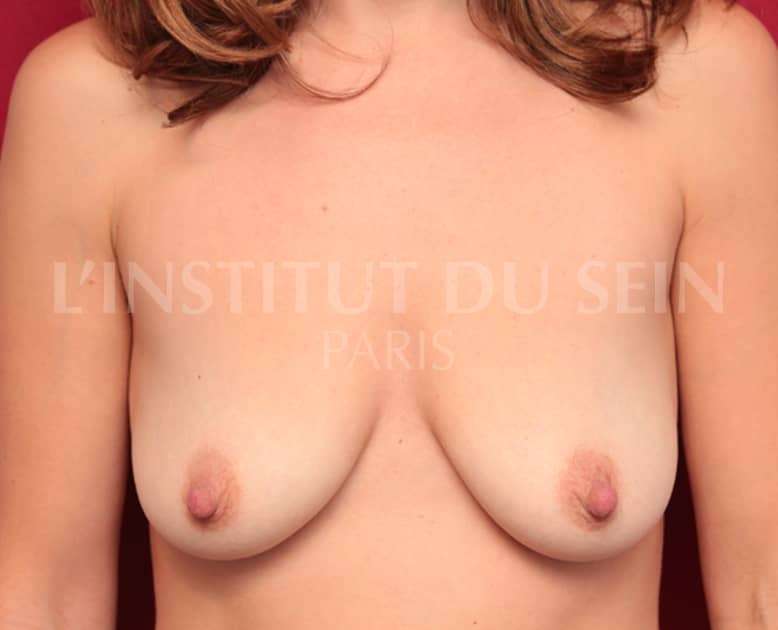
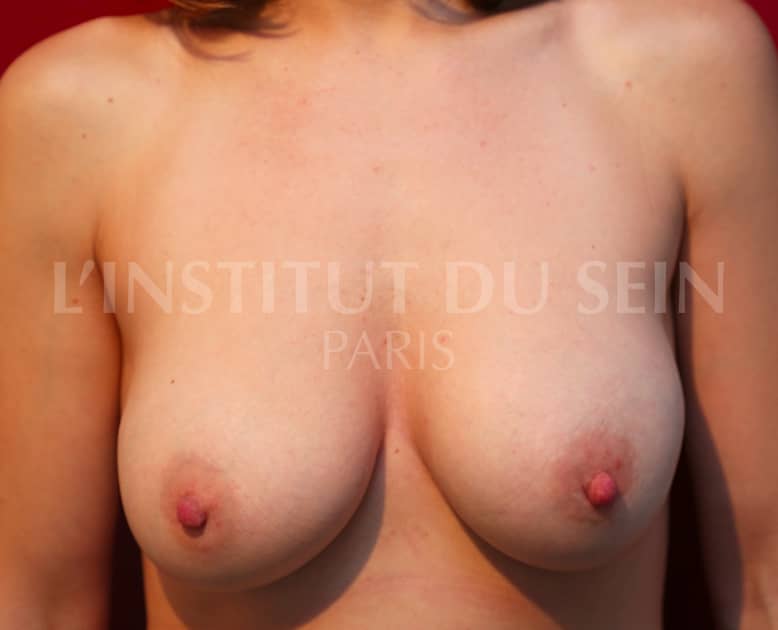


10. Augmentation by prosthesis without correction of ptosis.
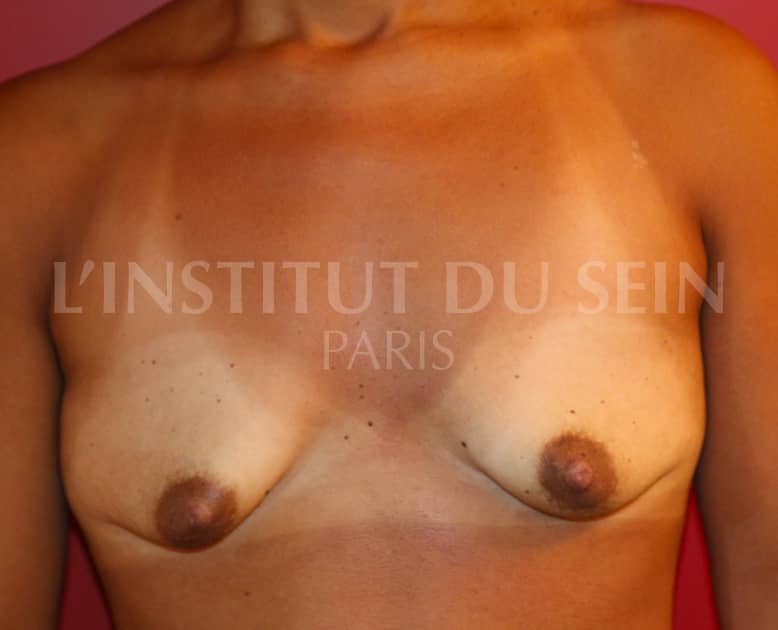

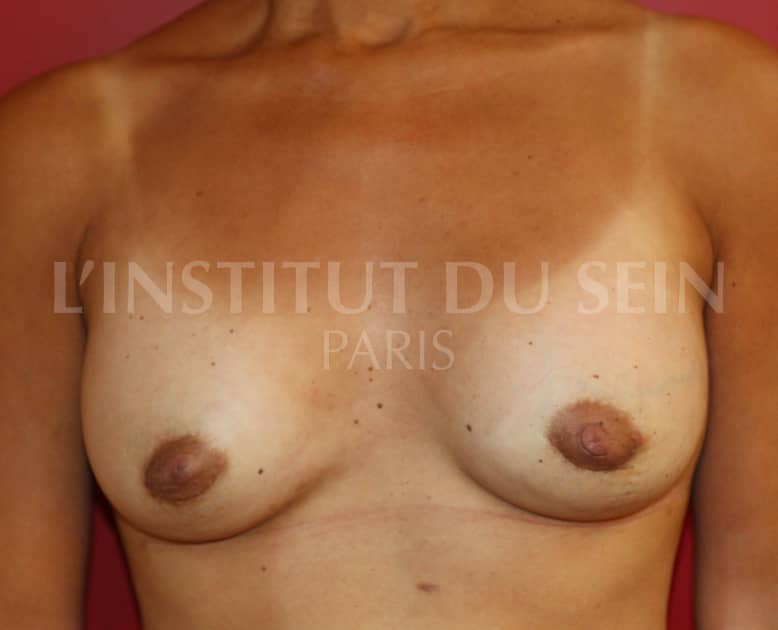
11. Augmentation by prostheses, lowering of the submammary groove. Lipofilling.
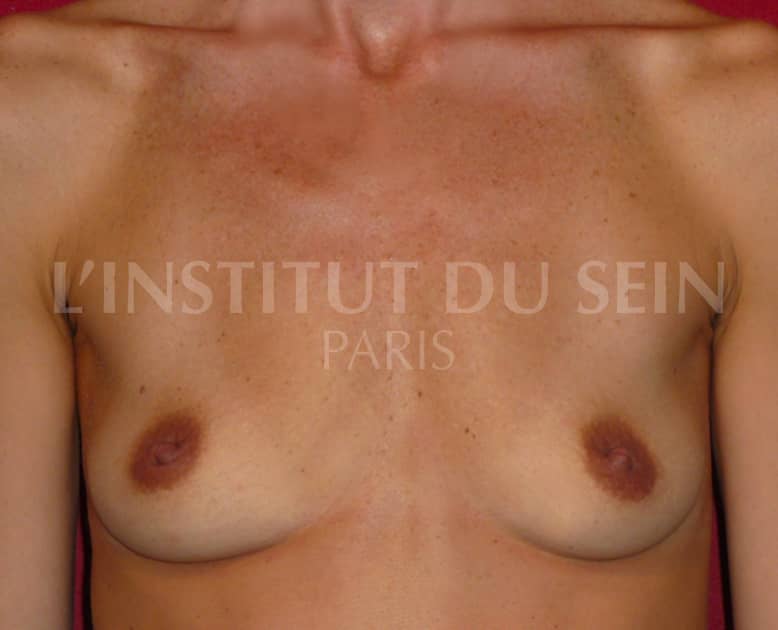
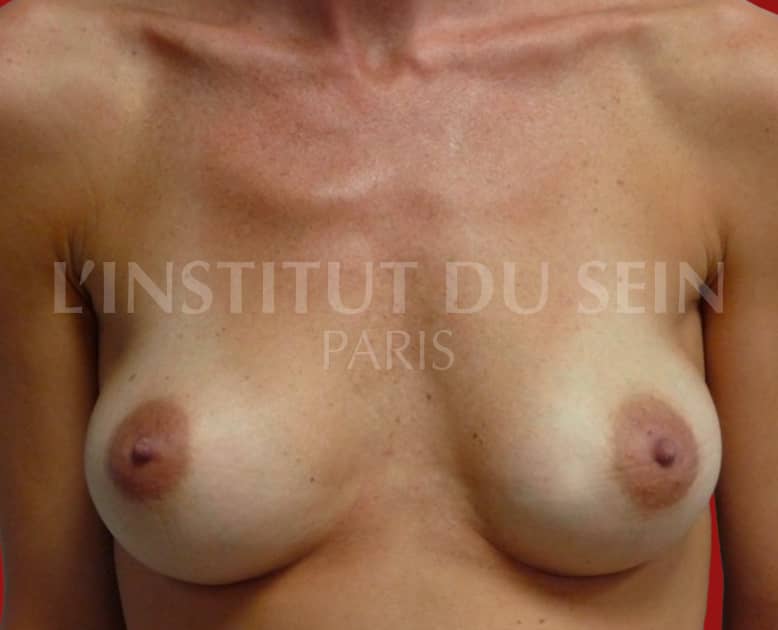
12. Increase per prosthesis.


13. Increase per prosthesis.
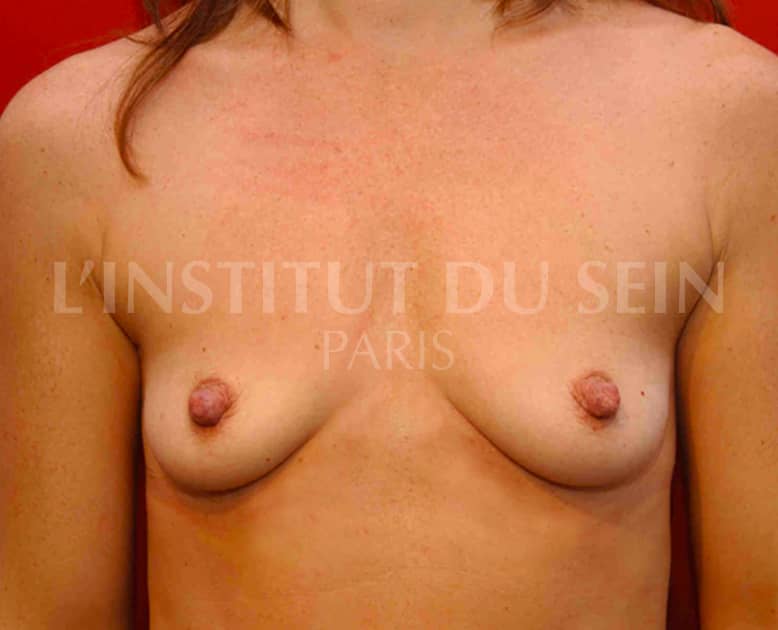
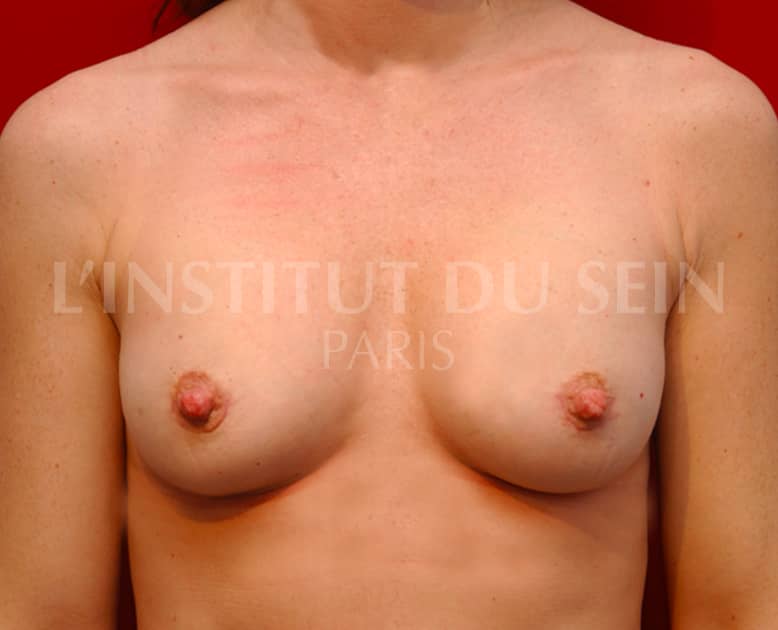
14. Increase per prosthesis.
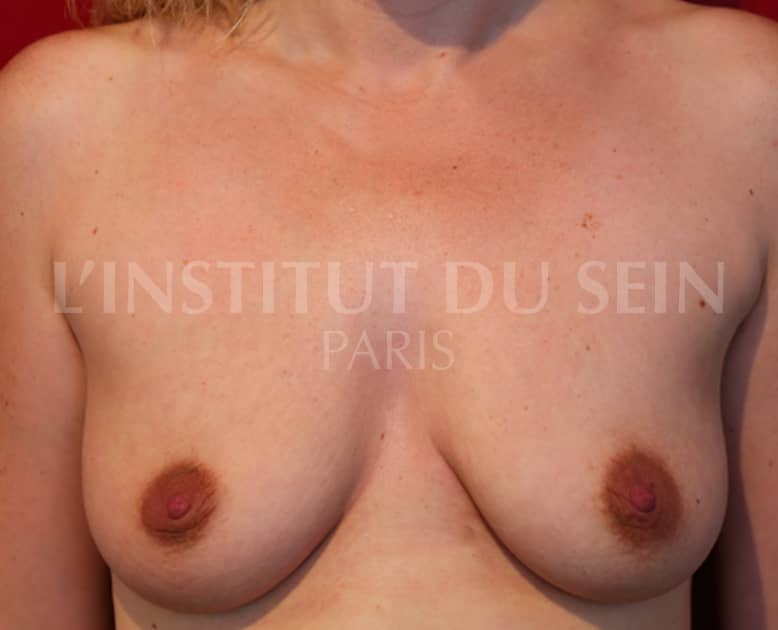

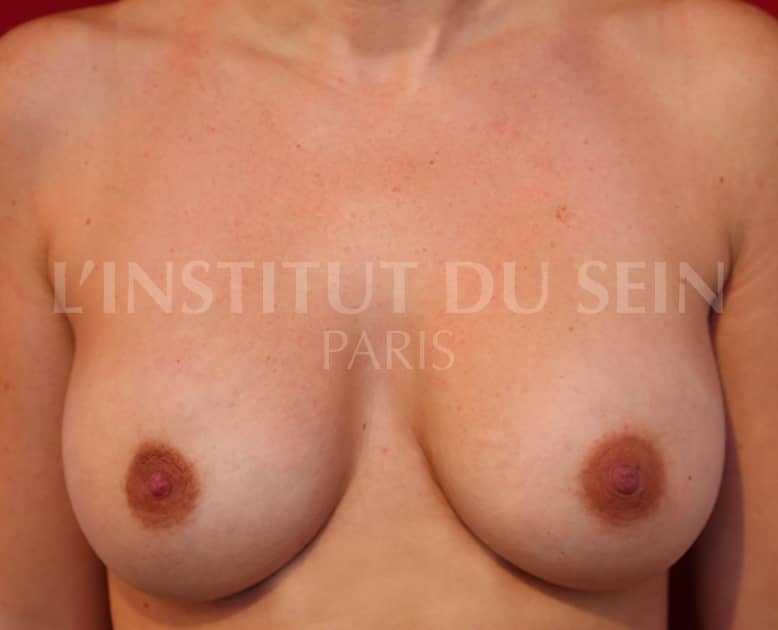
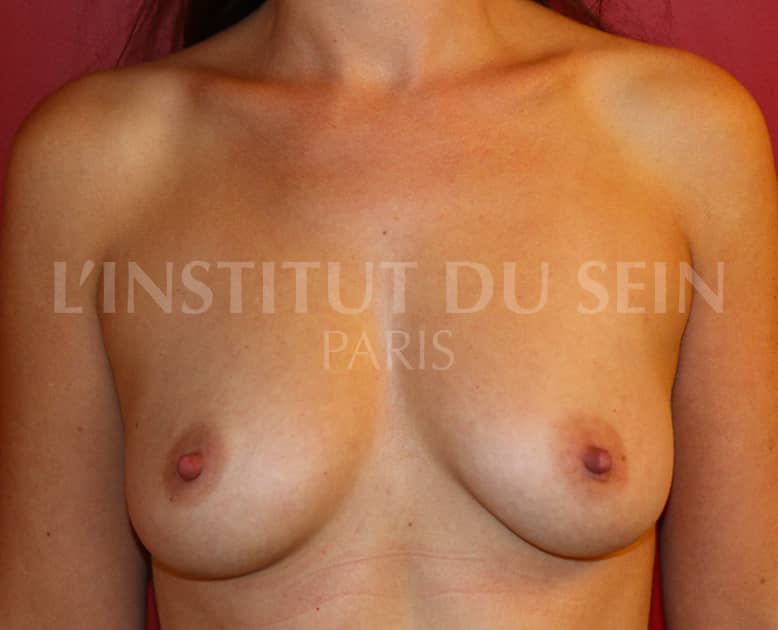
15. Augmentation by prosthesis without correction of ptosis.
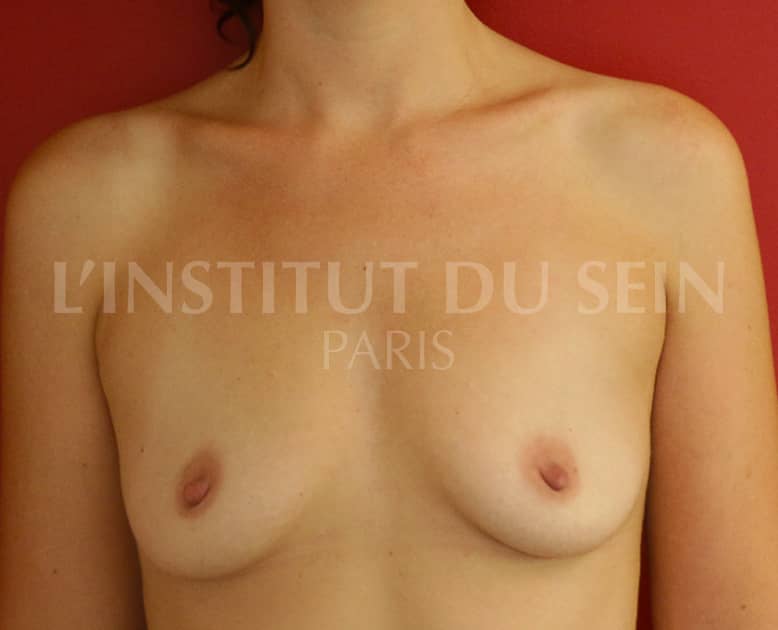

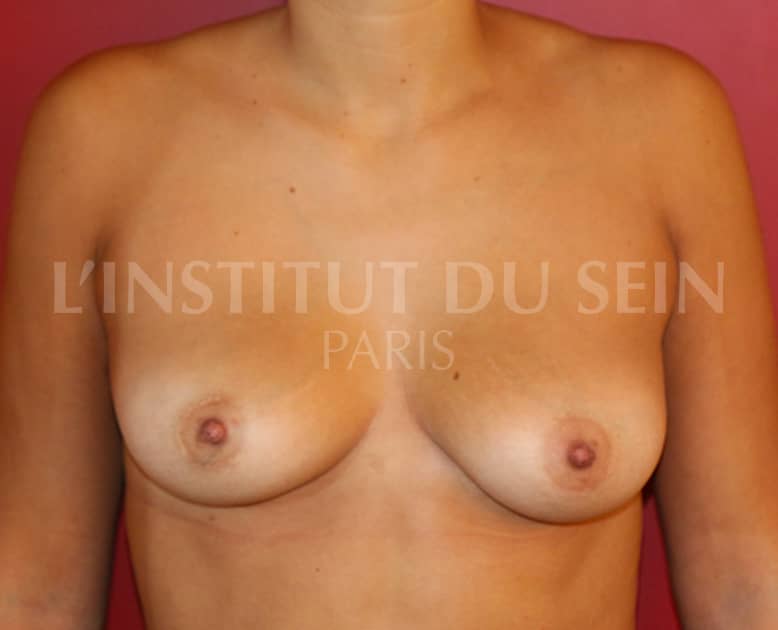
16. Augmentation by lipofilling.
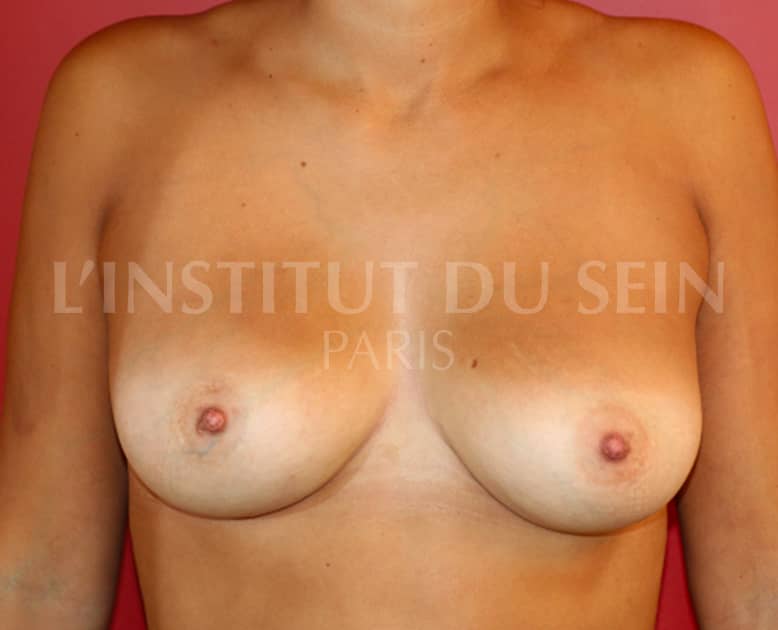
17. Correction of ptosis and asymmetry by lipofilling.
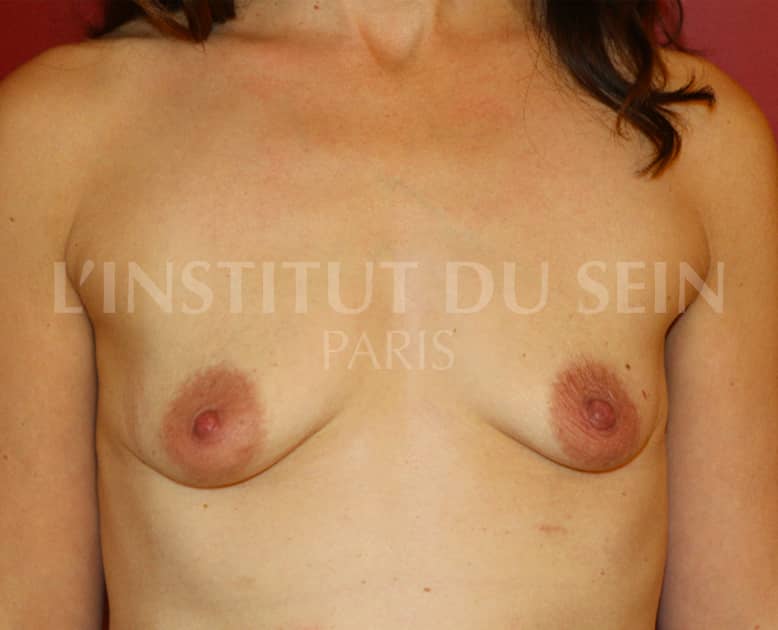
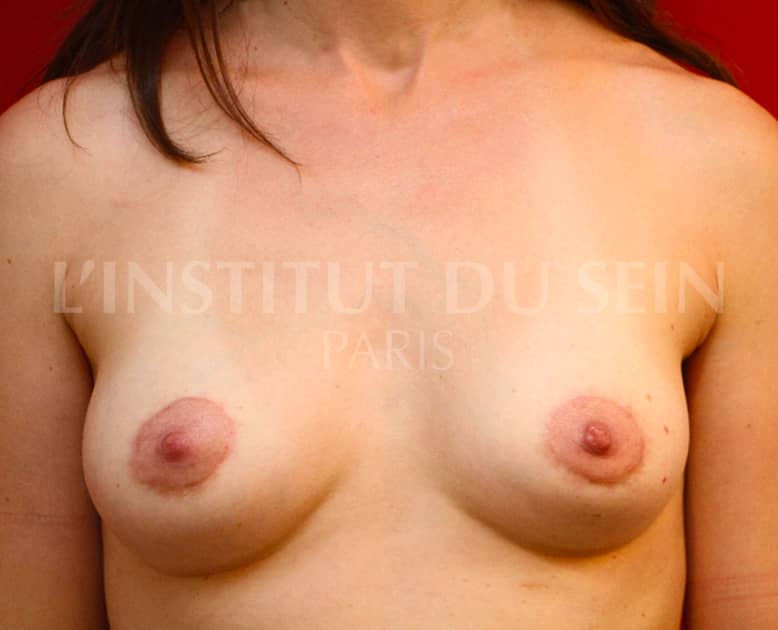
18. Augmentation by prosthesis. Correction of ptosis by periareolar scar (Round Block)
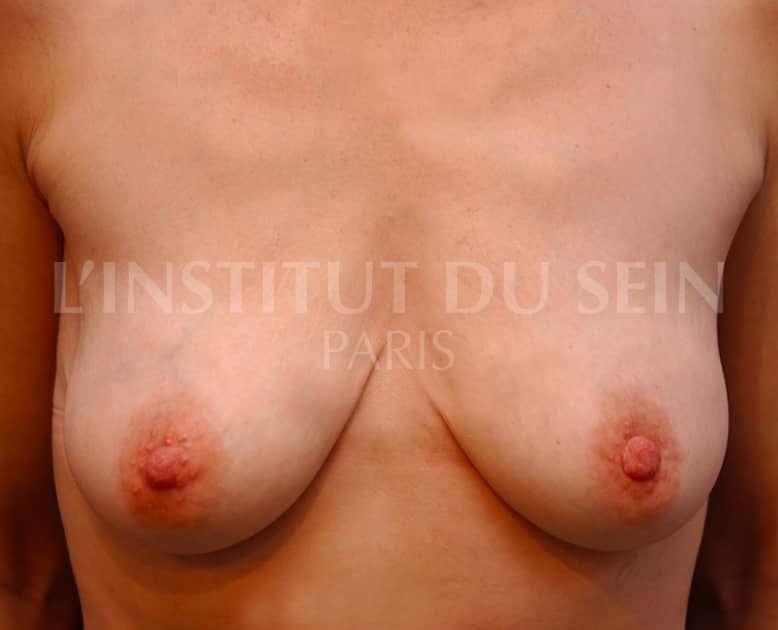
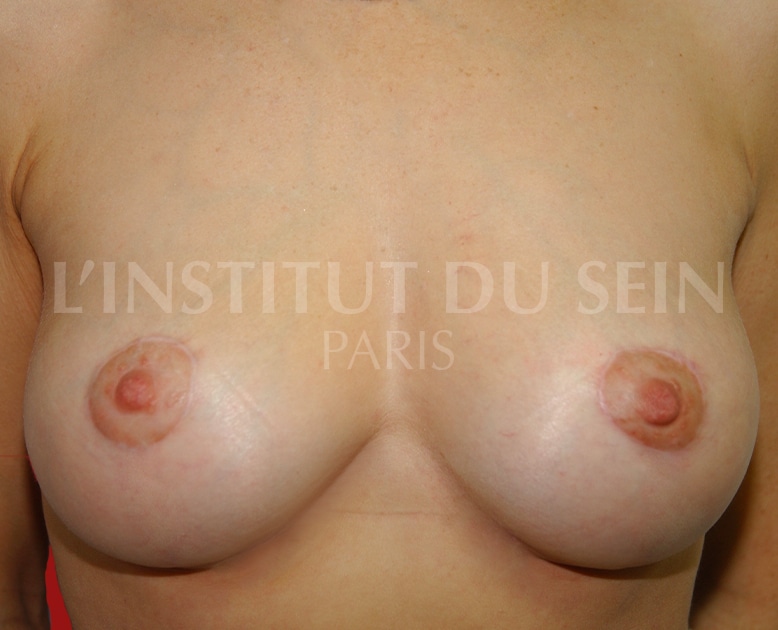
19. Augmentation by prosthesis. Treatment of ptosis by inverted T scar. Filling of the neckline by lipofilling.

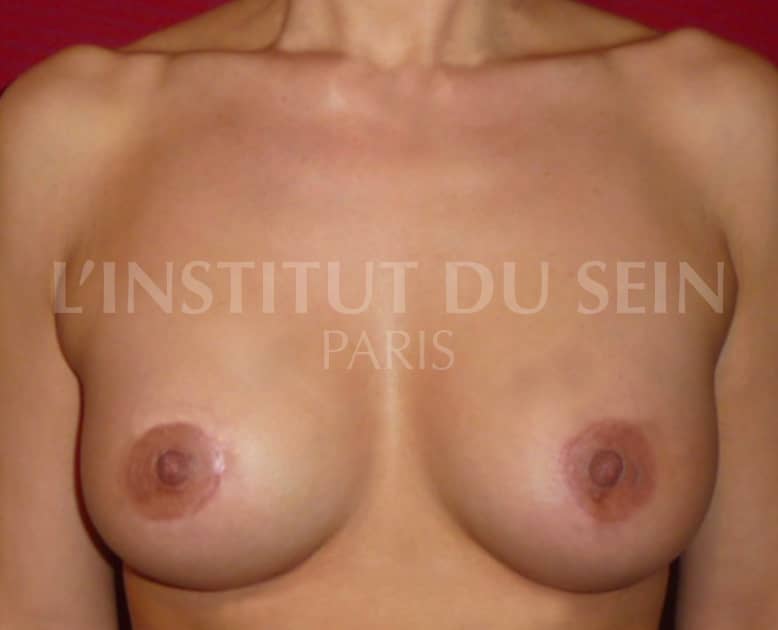
20. Augmentation by prosthesis. Treatment of ptosis and reduction in the size of the areolas by periareolar scar (Round Block).
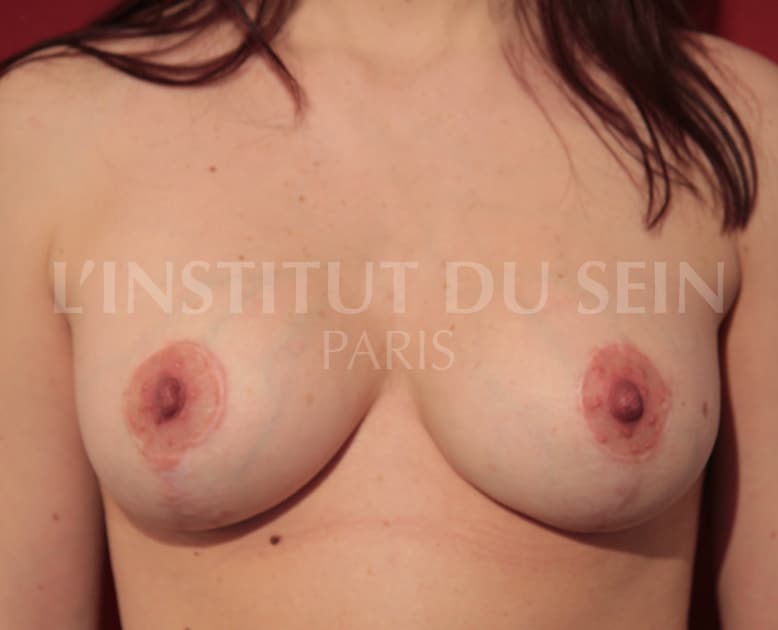
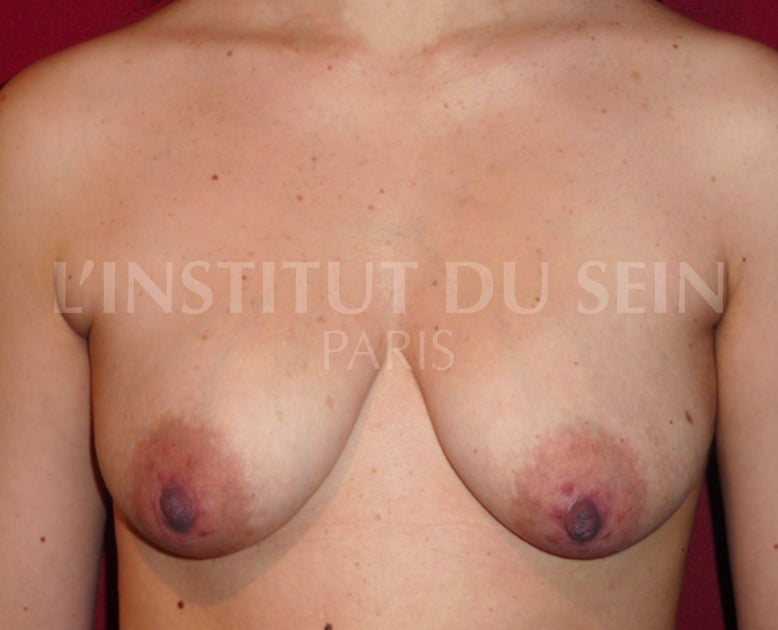

21. Augmentation by prosthesis and treatment of ptosis by inverted T scar
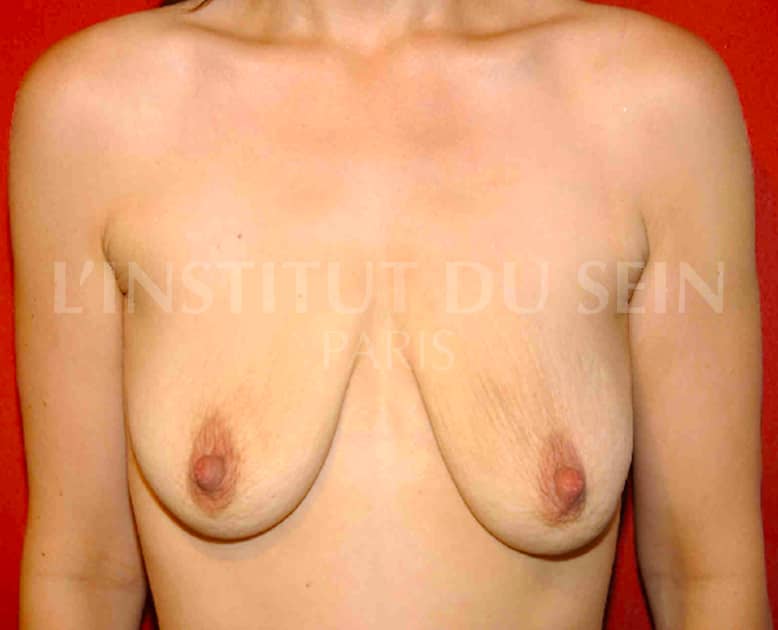
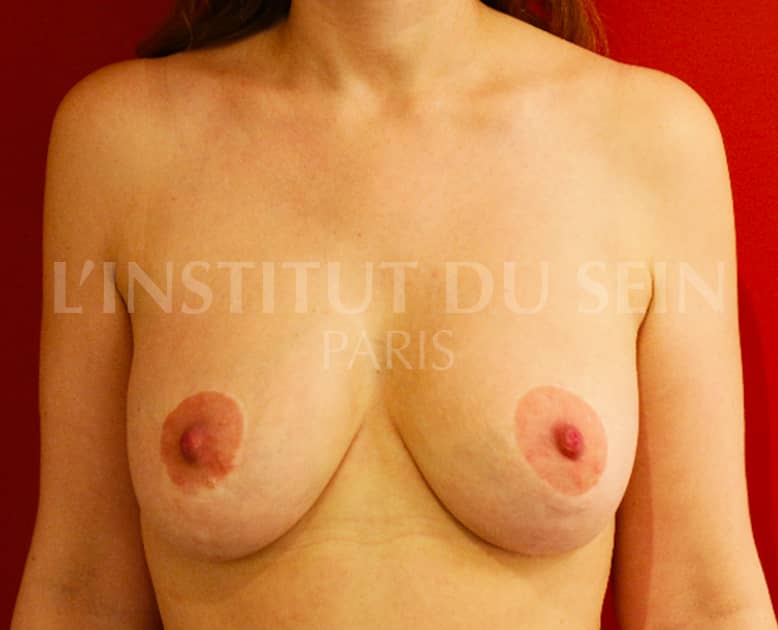
22. After weight loss of 50kg. Augmentation by prosthesis and treatment of ptosis by inverted T scar.
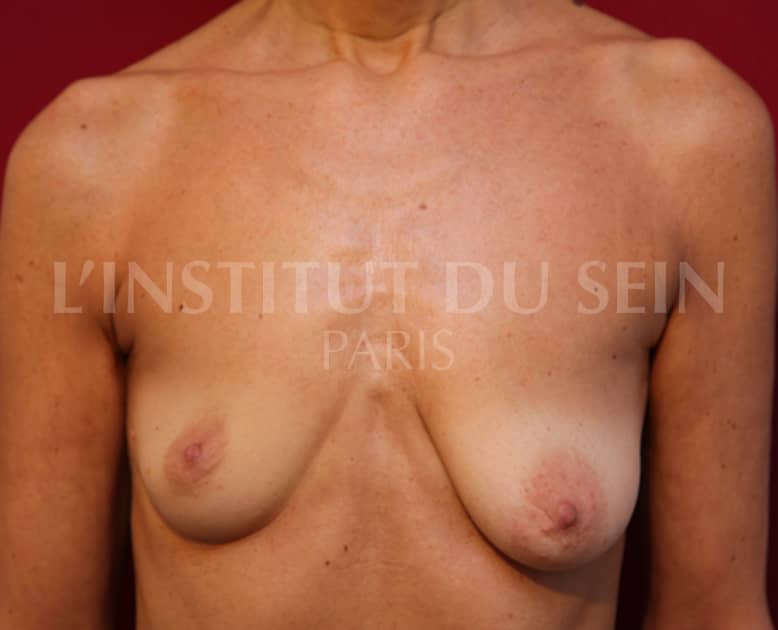
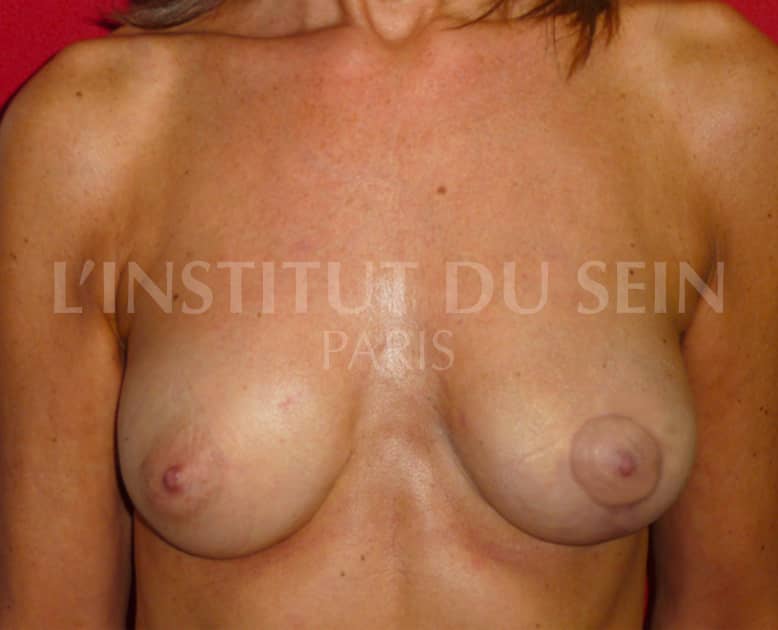
23. Augmentation by lipofilling. Treatment of left ptosis by inverted T scar.
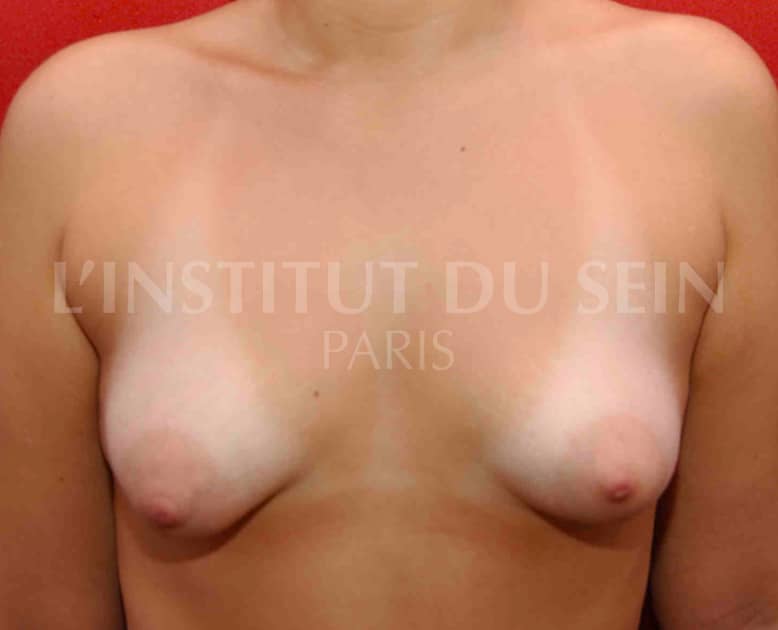
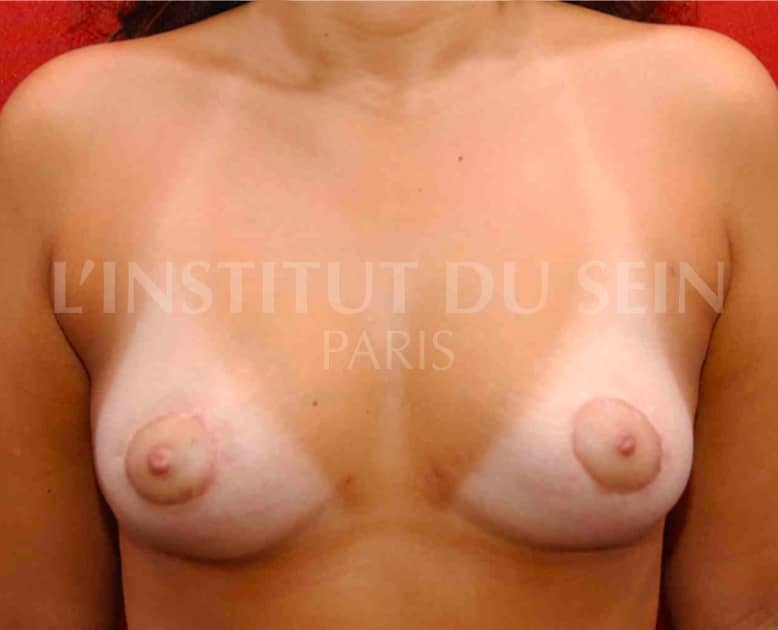
24. Augmentation by lipofilling. Lowering of the submammary folds. Repositioning of the areolas and reduction of their diameter by periareolar scar (Round Block).
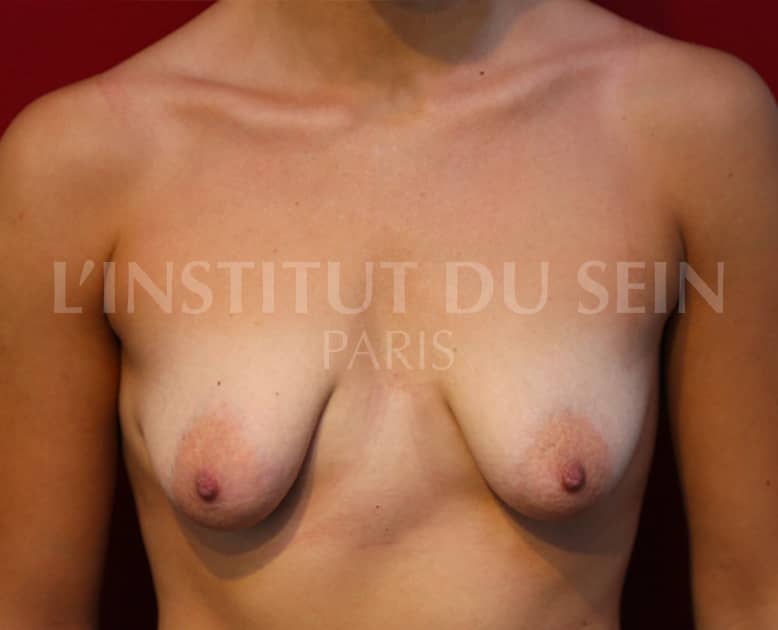
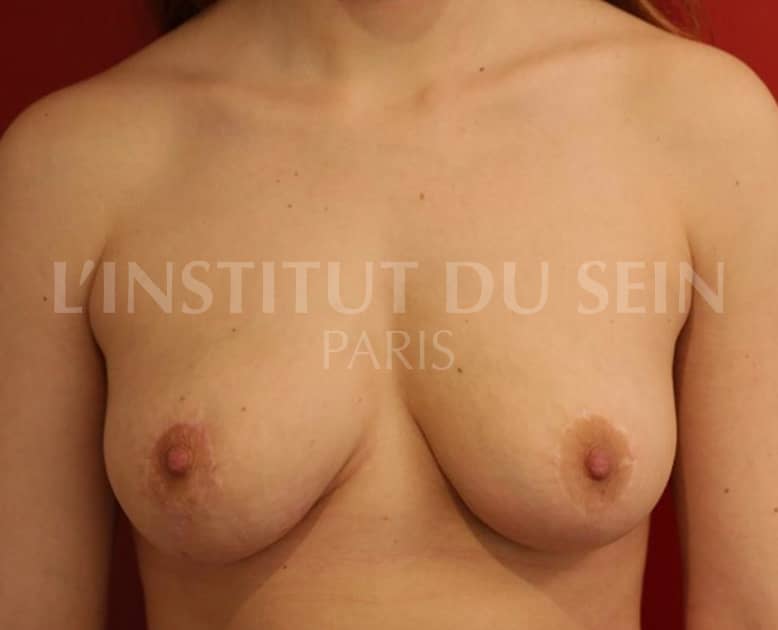
25. Treatment of ptosis by vertical and periareolar scar. Lipofilling.






Leave your comment